Comparing Attention and Cognitive Function in School Children across Noise Conditions: A Quasi-Experimental Study
- PMID: 29940716
- PMCID: PMC6018141
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2018.01.15
Comparing Attention and Cognitive Function in School Children across Noise Conditions: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Abstract
Objective: The effect of acute noise on cognitive function has long been a topic of study, yet these effects remain a serious problem for learning performance in school children.
Methods: From November 15, 2010 to December 8, 2010, we enrolled 268 students from three elementary schools (135 boys and 133 girls, 10-12 years old) in Ulsan, Korea. The study subjects were divided into two groups according to their test conditions (background versus additional noise), and tests were conducted using psychological examination tools. Chi-square tests and general linear models were used to assess the differences of impacts on cognition between the two groups.
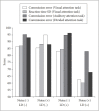
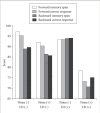
Results: After adjusting for socio-demographic covariates, the noise significantly affected the results of full-scale IQ, verbal IQ, Continuous Performance Test scores, and Children's Color Trails Test and Stroop test scores. The groups at high risk of learning difficulties were more affected by noise than low-risk groups.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that noise is hazardous to the attention and performance of elementary school students, particularly for groups at greater risk for poor academic achievement. Additional studies are needed to identify subject-specific levels of noise that can affect attention and cognitive function.
Keywords: Attention; Children; Cognition; Learning; Vulnerability; Noise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Link between depression and academic self-esteem in gifted children].Encephale. 2007 Jan-Feb;33(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(07)91554-7. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 17457290 French.
-
The Impact of Aircraft Noise on the Cognitive Function of Elementary School Students in Korea.Noise Health. 2023 Apr-Jun;25(117):83-91. doi: 10.4103/nah.nah_71_22. Noise Health. 2023. PMID: 37203125 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between blood manganese levels and children's attention, cognition, behavior, and academic performance--a nationwide cross-sectional study.Environ Res. 2013 Oct;126:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Environ Res. 2013. PMID: 23790803
-
Neuropsychological function in Tourette syndrome.Adv Neurol. 2001;85:103-11. Adv Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11530420 Review.
-
[Role of the implicit theories of intelligence in learning situations].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):456-63. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95460-7. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627050 Review. French.
Cited by
-
ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES ON ACADEMIC PROFICIENCY.Curr Epidemiol Rep. 2024 Mar;11(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s40471-023-00324-0. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Curr Epidemiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 40791788 Free PMC article.
-
Neurocognitive and Behavioral Outcomes of Chinese Survivors of Childhood Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 20;11:655669. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.655669. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33959507 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Noise Exposure on Cognitive Function in Children and Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis.NeuroSci. 2025 Mar 4;6(1):22. doi: 10.3390/neurosci6010022. NeuroSci. 2025. PMID: 40137867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noise and air pollution during Covid-19 lockdown easing around a school site.J Acoust Soc Am. 2022 Feb;151(2):881. doi: 10.1121/10.0009323. J Acoust Soc Am. 2022. PMID: 35232120 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a checklist for cognitive assessment requirements (CARE) based on a Delphi consensus study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 24;15(1):3146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87380-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39856338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe . Burden of Disease from Environmental Noise. Quantification of Healthy Life Years Lost in Europe. Geneva: WHO; 2011.
-
- Evans G, Lepore S. Nonauditory effects of noise on children: a critical review. Child Environ. 1993;10:31–51.
-
- Clark C, Sorqvist P. A 3 year update on the influence of noise on performance and behavior. Noise Health. 2012;14:292–296. - PubMed
-
- Clark C, Martin R, van Kempen E, Alfred T, Head J, Davies HW, et al. Exposure-effect relations between aircraft and road traffic noise exposure at school and reading comprehension: the RANCH project. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;163:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Stansfeld SA, Berglund B, Clark C, Lopez-Barrio I, Fischer P, Ohrstrom E, et al. Aircraft and road traffic noise and children’s cognition and health: a cross-national study. Lancet. 2005;365:1942–1949. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

