Exploration of 27 plasma immune markers: a cross-sectional comparison of 64 old psychiatric inpatients having unipolar major depression and 18 non-depressed old persons
- PMID: 29940870
- PMCID: PMC6020236
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-018-0836-x
Exploration of 27 plasma immune markers: a cross-sectional comparison of 64 old psychiatric inpatients having unipolar major depression and 18 non-depressed old persons
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of major depression (MD) according to population studies is the same for old (65 years and older) and younger adults. In contrast, an elevated proportion of old MD patients are hospitalized compared to younger adults with MD, indicating a need to expand the characteristics of old inpatients with MD. To illustrate this point, the association between inflammation and MD in old psychiatric inpatients is sparsely investigated even though an association between inflammation and treatment resistance among younger adults with MD has been reported. In this study, we aimed to explore the plasma concentrations of 27 immune markers in old inpatients with MD, and our purpose was to expand the understanding of inflammatory mechanisms in these patients.
Methods: Prior to electroconvulsive treatment of MD, we compared 64 inpatients with unipolar MD (mean age 75.2 years) and 18 non-depressed controls (mean age 78.0 years). Symptoms characterizing MD were assessed by the Hamilton Rating Scale of Depression (HRSD)-17, and the immune markers from peripheral blood plasma were analysed using multiplex assay technology. For statistical analysis of data, we used the independent samples median test, independent samples t-test, χ2-test, receiver operating characteristic curve analyses, stepwise discriminant analysis, and multivariate linear regression.
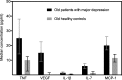
Results: Twenty-two immune markers representing pro- and anti-inflammatory, adaptive and trophic signalling had higher concentrations in the inpatients compared to the controls. Only the four immune markers IL-1β, IL-5, IL-10 and IL-15 had concentrations below the lower detection limit in a considerable portion (above 20%) of the patient cases. A combination of the concentration in plasma of TNF, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), IL-1β, IL-7 and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1, correctly classified 98.4% of the depressed patients and 83.3% of the non-depressed controls. Plasma concentration of TNF and VEGF were associated with the HRSD-17 scores (p = 0.017 and 0.005, respectively).
Conclusions: Our results indicate that several inflammatory mechanisms may be highly activated in old psychiatric inpatients with MD, and indicate that immune markers may contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of MD in old persons.
Trial registration: NCT01559324 ClinicalTrials.gov.
Keywords: Ageing immune system; Cytokines; Immune markers; Inflammation; Major depression; Old age.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Regional South East Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics in Norway has approved the study. Inclusions have been based strictly upon informed consent and the patient’s signature.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Persistent pro-inflammatory trait in elderly patients following treatment-resistant major depressive disorder: a longitudinal exploratory study.Nord J Psychiatry. 2025 Jan;79(1):42-51. doi: 10.1080/08039488.2024.2432981. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Nord J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39624907
-
IL-8 and the innate immunity as biomarkers in acute child and adolescent psychopathology.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Dec;62:233-42. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.08.017. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26325024
-
Immune suppression of IgG response against dairy proteins in major depression.BMC Psychiatry. 2017 Jul 24;17(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1431-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28738849 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of differences in IL-6 and IL-10 between people with and without depression: exploring the causes of heterogeneity.Brain Behav Immun. 2012 Oct;26(7):1180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.06.001. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2012. PMID: 22687336 Review.
-
Major depression and the NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule: validation in medically ill hospitalized patients.Int J Psychiatry Med. 1989;19(2):123-32. doi: 10.2190/vfmv-pc2v-a2hq-96yl. Int J Psychiatry Med. 1989. PMID: 2681026 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine profiles and diagnoses in elderly, hospitalized psychiatric patients.BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Sep 27;18(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1900-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30261848 Free PMC article.
-
Higher IL-6 and IL-4 plasma levels in depressed elderly women are influenced by diabetes mellitus.Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2024;46:e20220466. doi: 10.47626/2237-6089-2022-0466. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2024. PMID: 35796659 Free PMC article.
-
Altered serum interleukin-7 and interleukin-10 are associated with drug-free major depressive disorder.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020 Apr 28;10:2045125320916655. doi: 10.1177/2045125320916655. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32435448 Free PMC article.
-
The associations of psychological symptoms and cognitive patterns with pain and pain sensitization in people with hand osteoarthritis.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2022 May 6;4(2):100267. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2022.100267. eCollection 2022 Jun. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2022. PMID: 36475288 Free PMC article.
-
Late-Life Depression is Associated With Increased Levels of GDF-15, a Pro-Aging Mitokine.Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2023 Jan;31(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36153290 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

