Multiple morphogenic culture systems cause loss of resistance to cassava mosaic disease
- PMID: 29940871
- PMCID: PMC6020238
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-018-1354-x
Multiple morphogenic culture systems cause loss of resistance to cassava mosaic disease
Abstract
Background: Morphogenic culture systems are central to crop improvement programs that utilize transgenic and genome editing technologies. We previously reported that CMD2-type cassava (Manihot esculenta) cultivars lose resistance to cassava mosaic disease (CMD) when passed through somatic embryogenesis. As a result, these plants cannot be developed as products for deployment where CMD is endemic such as sub-Saharan Africa or the Indian sub-continent.
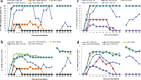
Result: In order to increase understanding of this phenomenon, 21 African cassava cultivars were screened for resistance to CMD after regeneration through somatic embryogenesis. Fifteen cultivars were shown to retain resistance to CMD through somatic embryogenesis, confirming that the existing transformation and gene editing systems can be employed in these genetic backgrounds without compromising resistance to geminivirus infection. CMD2-type cultivars were also subjected to plant regeneration via caulogenesis and meristem tip culture, resulting in 25-36% and 5-10% of regenerated plant lines losing resistance to CMD respectively.
Conclusions: This study provides clear evidence that multiple morphogenic systems can result in loss of resistance to CMD, and that somatic embryogenesis per se is not the underlying cause of this phenomenon. The information described here is critical for interpreting genomic, transcriptomic and epigenomic datasets aimed at understanding CMD resistance mechanisms in cassava.
Keywords: Cassava; Cassava mosaic disease; Meristem tip culture; Organogenesis; Somatic embryogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





References
-
- IITA . Annual report (International Institute of Tropical Agriculture) Ibadan: IITA; 1990.
-
- Okogbenin E, Moreno I, Tomkins J, Fauquet CM, Mkamilo G, Fregene M. Marker-assisted breeding for cassava mosaic disease resistance. In: Varshney R, Tuberosa R, editors. Translational genomics for crop breeding: biotic stress, Volume 1. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2013. pp. 291–325.
-
- Okogbenin E, Egesi CN, Olasanmi B, Ogundapo O, Kahya S, Hurtado P, et al. Molecular marker analysis and validation of resistance to cassava mosaic disease in elite cassava genotypes in Nigeria. Crop Sci. 2012;52:2576–2586. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2011.11.0586. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

