Admission homocysteine is an independent predictor of spontaneous reperfusion and early infarct-related artery patency before primary percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 29940881
- PMCID: PMC6020223
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-018-0868-3
Admission homocysteine is an independent predictor of spontaneous reperfusion and early infarct-related artery patency before primary percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Spontaneous reperfusion (SR) and early infarct related artery (IRA) patency before primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) might bring extra benefit for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). This study premilinarily screened the independent predictors of SR, and assessed the relationship between SR and plasma homocysteine (HCY).
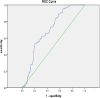
Methods: The medical records of 998 patients who were diagnosed as STEMI and underwent emergency coronary angiography were retrospectively studied, SR was defined as achievement of TIMI grade 3 flow in the IRA before PCI. The baseline characteristics, clinical manifestations and hematological variables were compared between SR and NSR group. Optimal cutoff point of HCY was calculated with receiving operating characteristics (ROC) analysis, multivariate logistic regression models were used to identify predictors of SR.
Results: 229 (22.95%) patients showed angiographic SR. For HCY, the area under the curve was 0.70 (95% CI: 0.63-0.77, P = 0.034), the optimized cut off point was 17.55 μmol/L. Preinfarct angina (95% CI: 1.61-5.65, P = 0.0005), plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) level (95% CI: 0.87-0.99, P = 0.016) and HCY < 17.55 μmol/L (95% CI: 2.43-8.72, P < 0.0001) were found to be independent predictors for SR.
Conclusion: In patients with STEMI, HCY < 17.55 μmol/L, preinfarct angina and plasma CRP level were independent predictors of SR.
Keywords: Homocysteine; Pre-interventional IRA patency; Predictor; ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; Spontaneous reperfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the China-Japan Friendship Hospital on Human Health Ethic Committee. Participation to the study was voluntary and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. We have received permission from the local hospital management to access patient medical records.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating the Correlation between Serum Amyloid A and Infarct-Related Artery Patency Prior to Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients.Angiology. 2024 Jul;75(6):585-594. doi: 10.1177/00033197231183031. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Angiology. 2024. PMID: 37402552
-
The relationship between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and infarct-related artery patency before mechanical reperfusion in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Coron Artery Dis. 2014 Mar;25(2):159-66. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000067. Coron Artery Dis. 2014. PMID: 24326783
-
Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio Can be a Predictor of Infarct-Related Artery Patency in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Angiology. 2015 Oct;66(9):831-6. doi: 10.1177/0003319715573658. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Angiology. 2015. PMID: 25712290
-
Post-cardiac injury syndrome in acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing PCI: a case report and literature review.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Dec 12;18(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0964-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 30541442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of no reflow and microvascular obstruction in the prognostic stratification of STEMI patients.Anatol J Cardiol. 2018 May;19(5):346-349. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2018.62343. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29537970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between uric acid-albumin ratio and spontaneous reperfusion in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2025 Feb 28;22(2):229-236. doi: 10.26599/1671-5411.2025.02.006. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40104830 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Plasma Total Homocysteine Levels and Mean Corrected TIMI Frame Count in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Nov 15;14:8161-8172. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S338938. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34815690 Free PMC article.
-
Associated factors of spontaneous reperfusion in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction before primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Afr Health Sci. 2025 Jun;25(2):85-93. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v25i2.12. Afr Health Sci. 2025. PMID: 40837650 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction III Flow in Patients With Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Not All Culprit Vessels Are Completely Occluded in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Cureus. 2020 Dec 12;12(12):e12036. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12036. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33457136 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Cytokines in Myocardial Infarction Are Associated With Coronary Blood Flow.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 15;13:837642. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.837642. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35242141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeymer U, Huber K, Fu Y, et al. Impact of TIMI 3 patency before primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction on clinical outcome: results from the ASSENT-4 PCI study. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2012;1(2):136–142. doi: 10.1177/2048872612447069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lekston A, Hudzik B, Szkodzinski J, et al. Spontaneous reperfusion before intervention improves immediate but not long-term prognosis in diabetic patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and multivessel coronary artery disease. Cardiol J. 2013;20(4):378–384. doi: 10.5603/CJ.2013.0096. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stone GW, Cox D, Garcia E, et al. Normal flow (TIMI-3) before mechanical reperfusion therapy is an independent determinant of survival in acute myocardial infarction: analysis from the primary angioplasty in myocardial infarction trials. Circulation. 2001;104(6):636–641. doi: 10.1161/hc3101.093701. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous