Estrogen-related receptors alpha, beta and gamma expression and function is associated with transcriptional repressor EZH2 in breast carcinoma
- PMID: 29940916
- PMCID: PMC6019302
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4586-0
Estrogen-related receptors alpha, beta and gamma expression and function is associated with transcriptional repressor EZH2 in breast carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Orphan nuclear receptors ERRα, ERRβ and ERRγ that belong to NR3B or type IV nuclear receptor family are well studied for their role in breast cancer pathophysiology. Their homology with the canonical estrogen receptor dictates their possible contributing role in mammary gland development and disease. Although function and regulation of ERRα, ERRγ and less about ERRβ is reported, role of histone methylation in their altered expression in cancer cells is not studied. Transcriptional activity of nuclear receptors depends on co-regulatory proteins. The present study for the first time gives an insight into regulation of estrogen-related receptors by histone methylation specifically through methyltransferase EZH2 in breast cancer.
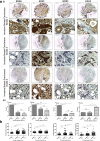
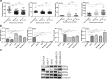
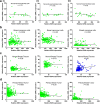
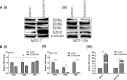
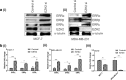
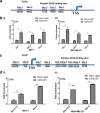
Methods: Expression of ERRα, ERRβ, ERRγ and EZH2 was assessed by immunohistochemistry in four identical tissue array slides that were prepared as per the protocol. The array slides were stained with ERRα, ERRβ, ERRγ and EZH2 simultaneously. Array data was correlated with expression in MERAV expression dataset. Pearson correlation coeficient r was calculated from the partial matrix expression values available at MERAV database to study the strength of association between EZH2 and three orphan nuclear receptors under study. By western blot and real time PCR, their correlated expression was studied in breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, T47D and MDA-MB-453 including normal breast epithelial MCF-10A cells at both protein and RNA level. Regulation of ERRα, ERRβ, ERRγ by EZH2 was further investigated upon overexpression and silencing of EZH2. The interaction between ERRs and EZH2 was validated in vivo by CHIP-qPCR.
Results: We found a negative correlation between estrogen-related receptors and Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2, a global repressor gene. Immunohistochemistry in primary breast tumors of different grades showed a correlated expression of estrogen-related receptors and EZH2. Their correlated expression was further validated using online MERAV expression dataset where a negative correlation of variable strengths was observed in breast cancer. Ectopic expression of EZH2 in low EZH2-expressing normal breast epithelial cells abrogated their expression and at the same time, its silencing enhanced the expression of estrogen-related receptors in cancerous cells. Global occupancy of EZH2 on ERRα and ERRβ was observed in-vivo.
Conclusion: Our findings identify EZH2 as a relevant coregulator for estrogen-related receptors in breast carcinoma.
Keywords: Breast cancer; EZH2; Orphan nuclear receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All breast cancer specimens were collected with written informed consents from the patients and were approved by Institutional Human Ethical Committee (Institute of Life Sciences, Bhubaneswar, India). All human tumor samples were handled in accordance with an approved protocol of human ethical committee.
Consent for publication
NA.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estrogen-related receptor alpha and estrogen-related receptor gamma associate with unfavorable and favorable biomarkers, respectively, in human breast cancer.Cancer Res. 2002 Nov 15;62(22):6510-8. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12438245
-
Estrogen receptor α dependent regulation of estrogen related receptor β and its role in cell cycle in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2018 May 30;18(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4528-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29843638 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of estrogen-related receptors beta and gamma (ERRbeta and ERRgamma) and their clinical significance in human prostate cancer.Cancer Sci. 2010 Mar;101(3):646-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01451.x. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20128821 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-related receptors as emerging targets in cancer and metabolic disorders.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(3):203-15. doi: 10.2174/1568026610606030203. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16515477 Review.
-
Estrogen-related receptor β (ERRβ) - renaissance receptor or receptor renaissance?Nucl Recept Signal. 2016 Jun 21;14:e002. doi: 10.1621/nrs.14002. eCollection 2016. Nucl Recept Signal. 2016. PMID: 27507929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NEDDylation negatively regulates ERRβ expression to promote breast cancer tumorigenesis and progression.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 24;11(8):703. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02838-7. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32839427 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted Transcriptional Network of Estrogen-Related Receptor Alpha in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;24(5):4265. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054265. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Analysis of a Risk Score System Predicting Prognosis and a ceRNA Network for Differentially Expressed lncRNAs in Multiple Myeloma.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 27;11:934. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00934. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33193574 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-related receptor alpha in select host functions and cancer: new frontiers.Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 May;477(5):1349-1359. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04380-w. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35138514 Review.
-
Exploring the Biological Activity and Mechanism of Xenoestrogens and Phytoestrogens in Cancers: Emerging Methods and Concepts.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8798. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168798. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giguere V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev. 1999;20(5):689–725. - PubMed
-
- Audet-Walsh E, Papadopoli DJ, Gravel SP, Yee T, Bridon G, Caron M, Bourque G, Giguere V, St-Pierre J. The PGC-1alpha/ERRalpha Axis represses one-carbon metabolism and promotes sensitivity to anti-folate therapy in breast Cancer. Cell Rep. 2016;14(4):920–931. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.086. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

