Is Xpert MTB/RIF appropriate for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy with pleural fluid samples? A systematic review
- PMID: 29940951
- PMCID: PMC6019837
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3196-4
Is Xpert MTB/RIF appropriate for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy with pleural fluid samples? A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Tuberculous pleurisy (TP) presents a diagnostic problem due to the limitations of traditional diagnostic methods. Different studies with the Xpert MTB/RIF assay have drawn variable conclusions about its values in TP diagnosis. We conducted a meta-analysis to assess whether the Xpert MTB/RIF assay is appropriate for the diagnosis of TP using pleural fluid samples.
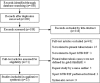
Methods: A systematic search of four literature databases in English and Chinese language was performed to identify studies involving the use of Xpert MTB/RIF in patients with TP confirmed by plural biopsy and/or mycobacterial culture. Pooled sensitivity, specificity and accordance proportion were calculated, and the forest plots were generated to assess the accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF for TP diagnosis.
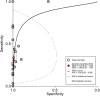
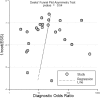
Results: We identified 23 studies meeting our inclusion criteria. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF were 30% (95% CI: 21-42%, I2 = 87.93%) and 99% (95% CI: 97-100%, I2 = 96.20%), respectively, and the area under the SROC curve (AUC) of Xpert MTB/RIF was 0.86 (95% CI: 0.83-0.89). Compared with drug susceptibility testing (DST), the pooled accordance rate of Xpert MTB/RIF in detecting rifampicin-susceptible cases and rifampicin-resistant cases was 99% (95% CI: 95-104%, I2 = 8.7%) and 94% (95% CI: 86-102%), respectively.
Conclusions: Our analysis suggests that the Xpert MTB/RIF assay is of limited value as a screening test for TP but has a high potential for confirming TP diagnosis and differentiating TP from non-TB diseases using pleural fluid samples.
Keywords: Pleural fluid; Rifampicin resistance; Systematic review; Tuberculous pleurisy; Xpert MTB/RIF.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All analyses were based on previous published studies, thus no ethical approval and patient consent are required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests. No competing interests exists in this study due to commercial or other associations (e.g., pharmaceutical stock ownership, consultancy, advisory board membership, relevant patents, or research funding). No competing interests exists in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all of the authors for publication, all authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere in whole or in part.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2017. Available: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/259366/1/9789241565516-eng.pdf. Accessed 26 May 2018.
-
- World Health Organization. Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resitance: Xpert MTB/RIF System. Available: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241501545_eng.pdf. Accessed 26 May 2018. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF system for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonaryTB in adults and children. Available: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/112472/1/9789241506335_eng.pdf. Accessed 26 May 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

