ER-α36 mediates cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells through EGFR/HER-2/ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 29940998
- PMCID: PMC6019204
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0798-z
ER-α36 mediates cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells through EGFR/HER-2/ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: ER-α36, a novel ER-α66 variant, has been demonstrated to promote tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. However, the role and mechanisms of ER-α36 in cisplatin resistance of breast cancer cells remain unclear. This study investigates the expression and role of ER-α36 in cisplatin resistance of breast cancer cells and elucidates its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: The expression of ER-α36 and the proteins involved in nongenomic estrogen signaling was evaluated by western blot analysis. Cisplatin sensitivity was explored by CCK-8 assay, monolayer colony formation assay and apoptosis assays, respectively. ER-α36 siRNAs/shRNAs and overexpression vector were transfected into cells to down-regulate or up-regulate ER-α36 expression. Loss-and gain-of function assays were performed to investigate the role of ER-α36 in cisplatin sensitivity. The interaction between ER-α36 and EGFR/HER-2 were detected using CoIP. A mouse xenograft model of breast cancer was established to verify the role of ER-α36 in vivo.
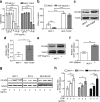
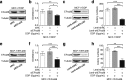
Results: ER-α36 is expressed at higher levels in cisplatin-resistant breast cancer cells compared to cisplatin sensitive cells. Cisplatin induced up-regulation of ER-α36 in a dose-dependent manner in breast cancer cells. Overexpression of ER-α36 leaded to cell resistant to cisplatin and knockdown of ER-α36 in cisplatin-resistant breast cancer cells restored cisplatin sensitivity. The up-regulation of ER-α36 resulted in increased activation of nongenomic estrogen signaling, which was responsible for cisplatin resistance. Disruption of ER-α36-mediated nongenomic estrogen signaling with kinase inhibitors significantly inhibited cisplatin-induced expression of ER-α36 and increased cisplatin sensitivity. The in vivo experiment also confirmed that up-regulation of ER-α36 attenuated cisplatin sensitivity in a mouse xenograft model of breast cancer.
Conclusions: The results for the first time demonstrated that ER-α36 mediates cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells through nongenomic estrogen signaling, suggesting that ER-α36 may serve as a novel target for cisplatin resistance and a potential indicator of cisplatin sensitivity in breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cisplatin resistance; EGFR; ER-α36; HER-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
This study has been conducted in accordance with ethical standards and the national and international guidelines. All animal experiments were carried out according to the protocol approved by the Third Military Medical University Guidelines for Use and Care of Animals. No human samples were involved in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Estrogen receptor-α36 is involved in development of acquired tamoxifen resistance via regulating the growth status switch in breast cancer cells.Mol Oncol. 2013 Jun;7(3):611-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23499324 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor-α36 is involved in pterostilbene-induced apoptosis and anti-proliferation in in vitro and in vivo breast cancer.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 15;9(8):e104459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104459. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25127034 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor-α variant, ER-α36, is involved in tamoxifen resistance and estrogen hypersensitivity.Endocrinology. 2013 Jun;154(6):1990-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1116. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23546601
-
Roles of the ER-α36-EGFR/HER2 positive regulatory loops in tamoxifen resistance.Steroids. 2016 Jul;111:95-99. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2016.01.019. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Steroids. 2016. PMID: 26884313 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor alpha-36 (ER-α36): A new player in human breast cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 3:193-206. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25917453 Review.
Cited by
-
Research on the biological mechanism and potential application of CEMIP.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 18;14:1222425. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1222425. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37662915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keratin 24 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer.Pathobiology. 2025 Apr 19:1-14. doi: 10.1159/000546022. Online ahead of print. Pathobiology. 2025. PMID: 40254011 Free PMC article.
-
Rewiring of the Endocrine Network in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:830894. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.830894. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPV1 inhibition overcomes cisplatin resistance by blocking autophagy-mediated hyperactivation of EGFR signaling pathway.Nat Commun. 2023 May 10;14(1):2691. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38318-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37165076 Free PMC article.
-
Aldolase A promotes cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance via the EGFR pathway in gastric cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Sep 15;14(9):6586-6595. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36247245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilmes A, Bielow C, Ranninger C, Bellwon P, Aschauer L, Limonciel A, Chassaigne H, Kristl T, Aiche S, Huber CG, Guillou C, Hewitt P, et al. Mechanism of cisplatin proximal tubule toxicity revealed by integrating transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics and biokinetics. Toxicol in Vitro. 2015;30(1PtA):117–127. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.10.006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

