Pharmacokinetics and Comprehensive Analysis of the Tissue Distribution of Eravacycline in Rabbits
- PMID: 29941646
- PMCID: PMC6125520
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00275-18
Pharmacokinetics and Comprehensive Analysis of the Tissue Distribution of Eravacycline in Rabbits
Abstract
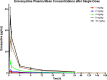
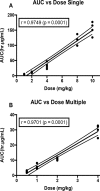
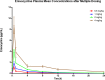
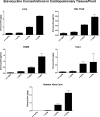
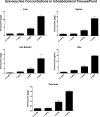
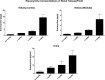
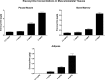
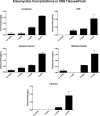
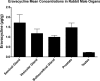
Eravacycline (7-fluoro-9-pyrrolidinoacetamido-6-demethyl-6-deoxytetracycline or TP-434) is a novel, fully synthetic broad-spectrum fluorocycline with potent activity against Gram-positive bacteria, anaerobes, and multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae We characterized the plasma pharmacokinetics of eravacycline and conducted a comprehensive analysis of the eravacycline tissue distribution in rabbits after multiple-day dosing. For single-dose pharmacokinetic analysis, eravacycline was administered to New Zealand White (NZW) rabbits at 1, 2, 4, 8, and 10 mg/kg of body weight intravenously (i.v.) once a day (QD) (n = 20). For multidose pharmacokinetic analysis, eravacycline was administered at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mg/kg i.v. QD (n = 20) for 6 days. Eravacycline concentrations in plasma and tissues were analyzed by a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay. Mean areas under the concentration-time curves (AUCs) following a single eravacycline dose ranged from 5.39 μg · h/ml to 183.53 μg · h/ml. Within the multidose study, mean AUCs ranged from 2.53 μg · h/ml to 29.89 μg · h/ml. AUCs correlated linearly within the dosage range (r = 0.97; P = 0.0001). In the cardiopulmonary system, the concentrations were the highest in the lung, followed by the heart > pulmonary alveolar macrophages > bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; for the intra-abdominal system, the concentrations were the highest in bile, followed by the liver > gallbladder > spleen > pancreas; for the renal system, the concentrations were the highest in urine, followed by those in the renal cortex > renal medulla; for the musculoskeletal tissues, the concentrations were the highest in muscle psoas, followed by those in the bone marrow > adipose tissue; for the central nervous system, the concentrations were the highest in cerebrum, followed by those in the aqueous humor > cerebrospinal fluid > choroid > vitreous. The prostate and seminal vesicles demonstrated relatively high mean concentrations. The plasma pharmacokinetic profile of 0.5 to 4 mg/kg in NZW rabbits yields an exposure comparable to that in humans (1 or 2 mg/kg every 12 h) and demonstrates target tissue concentrations in most sites.
Keywords: eravacycline; pharmacokinetics; rabbits; tissue distribution.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review of Eravacycline, a Novel Fluorocycline Antibacterial Agent.Drugs. 2016 Apr;76(5):567-88. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0545-8. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26863149 Review.
-
Antibacterial activity of eravacycline (TP-434), a novel fluorocycline, against hospital and community pathogens.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Nov;57(11):5548-58. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01288-13. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23979750 Free PMC article.
-
Eravacycline, a newly approved fluorocycline.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Oct;38(10):1787-1794. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03590-3. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31175478 Review.
-
Antibacterial Efficacy of Eravacycline In Vivo against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Organisms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):5001-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00366-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27353265 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Doses of Eravacycline.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Oct 24;62(11):e01174-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01174-18. Print 2018 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30150464 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
In vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Dose Optimization of Eravacycline and Other Tetracycline Derivatives Against Levofloxacin-Non-Susceptible and/or Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Sep 8;16:6005-6015. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S425061. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37705512 Free PMC article.
-
New Antibiotics for the Treatment of Nosocomial Central Nervous System Infections.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jan 7;13(1):58. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13010058. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Eravacycline.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Sep;58(9):1149-1153. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00767-z. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 31049869 Review.
-
Inadequate Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentrations of Available Salvage Agents Further Impedes the Optimal Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Meningitis and Bacteremia.Infect Dis Rep. 2021 Sep 8;13(3):843-854. doi: 10.3390/idr13030076. Infect Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34563001 Free PMC article.
-
Acinetobacter baumannii treatment strategies: a review of therapeutic challenges and considerations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Aug 6;69(8):e0106324. doi: 10.1128/aac.01063-24. Epub 2025 Jul 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40631987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiao XY, Hunt DK, Zhou J, Clark RB, Dunwoody N, Fyfe C, Grossman TH, O'Brien WJ, Plamondon L, Ronn M, Sun C, Zhang WY, Sutcliffe JA. 2012. Fluorocyclines. 1. 7-Fluoro-9-pyrrolidinoacetamido-6-demethyl-6-deoxytetracycline: a potent, broad spectrum antibacterial agent. J Med Chem 55:597–605. doi:10.1021/jm201465w. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

