Genistein Improves Liver Damage in Male Mice Exposed to Morphine
- PMID: 29941714
- PMCID: PMC6032674
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.235117
Genistein Improves Liver Damage in Male Mice Exposed to Morphine
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Genistein Improves Liver Damage in Male Mice Exposed to Morphine.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Jul 20;131(14):1764. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.235870. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29998906 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Morphine is commonly used to treat severe pain. This substance is significantly metabolized in the liver and causes disturbing effects. Genistein is an isoflavone and has antioxidant properties. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of genistein against morphine damages on mouse liver.
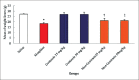
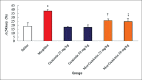
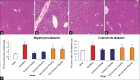
Methods: Between May 2017 and March 2018, 48 male mice were divided into six groups (n = 8 in each group). Various doses of genistein (25 and 50 mg/kg) and morphine plus genistein (25 and 50 mg/kg) were administered intraperitoneally to 48 male mice for 20 consequent days. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), serum nitric oxide (NO) levels, liver weight, and the diameter of hepatocytes and central hepatic vein were studied and compared using one-way analysis of variance.
Results: Morphine administration significantly increased the mean diameter of the central hepatic vein (22.76 ± 1.9 μm vs. 15.04 ± 0.60 μm, χ2 = 21.814, P = 0.001) and hepatocytes (3.03 ± 0.10 μm vs. 1.10 ± 0.05 μm, χ2 = 9.873, P = 0.001) respectively, blood serum NO level (38.00% ± 2.09% vs. 18.72% ± 4.40%, χ2 = 20.404, P < 0.001), liver enzyme level (AST: 111.80 ± 5.10 ng/ml vs. 81.93 ± 2.20 ng/ml, χ2 = 32.201, P < 0.0001; ALT: 45.14 ± 4.10 ng/ml vs. 35.49 ± 2.50 ng/ml, χ2 = 18.203, P < 0.0001; and ALP: 3.28 ± 0.20 ng/ml vs. 2.14 ± 0.10, χ2 = 5.04, P < 0.0001, respectively), and decreased liver weight (18.50 ± 0.90 g vs. 27.15 ± 0.50 g, χ2 = 22.415, P = 0.001) compared to saline group (0.535-0.750, P < 0.0001). However, administration of genistein plus morphine significantly enhanced liver weight (25 mg/kg: 21.15 ± 2.13 g vs. 18.50 ± 0.90 g, χ2 = 19.251, P < 0.0001; 50 mg/kg: 21.20 ± 1.00 g vs. 18.5 ± 0.9 g, χ2 = 19.502, P < 0.0001, respectively) and reduced the mean diameter of hepatocyte (25 mg/kg: 2.17 ± 0.30 μm vs. 3.03 ± 0.10 μm, χ2 = 22.780, P = 0.001; 50 mg/kg: 2.01 ± 0.20 μm vs. 3.03 ± 0.10 μm χ2 = 7.120, P = 0.001, respectively), central hepatic vein (25 mg/kg: 19.53 ± 1.00 μm vs. 22.76 ± 1.90 μm, χ2 = 20.681, P = 0.001; 50 mg/kg: 19.44 ± 1.20 μm vs. 22.76 ± 1.90 μm, χ2 = 18.451, P = 0.001, respectively), AST (25 mg/kg: 95.40 ± 5.20 ng/ml vs. 111.80 ± 5.010 ng/ml, P < 0.0001; 50 mg/kg: 90.78 ± 6.00 ng/ml vs. 111.80 ± 5.10 ng/ml, χ2 = 17.112, P < 0.0001, respectively), ALT (25 mg/kg: 35.78 ± 5.01 ng/ml vs. 45.14 ± 4.10 ng/ml, χ2 = 15.320, P < 0.0001; 50 mg/kg: 33.78 ± 2.60 ng/ml vs. 45.14 ± 4.10 ng/ml, χ2 = 14.023, P < 0.0001, respectively), ALP (25 mg/kg: 2.35 ± 0.30 ng/ml vs. 3.28 ± 0.20 ng/ml, χ2 = 4.101, P < 0.0001; 50 mg/kg: 2.34 ± 0.10 ng/ml vs. 3.28 ± 0.20 ng/ml, χ2 = 2.033, P < 0.0001, respectively), and NO levels (25 mg/kg: 25.92% ± 2.30% vs. 38% ± 2.09%, χ2 = 17.103, P < 0.0001; 50 mg/kg: 24.74% ± 4.10% vs. 38% ± 2.09%, χ2 = 25.050, P = 0.001, respectively) compared to morphine group.
Conclusion: It seems that genistein administration might improve liver damages induced by morphine in mice.
Keywords: Genistein; Liver Damage; Morphine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Thymoquinone Against Morphine-induced Damages on Male Mice Liver.Int J Prev Med. 2018 Jan 29;9:8. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_144_16. eCollection 2018. Int J Prev Med. 2018. PMID: 29441185 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of crocin on liver toxicity induced by morphine.Res Pharm Sci. 2016 Mar-Apr;11(2):120-9. Res Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27168751 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Crocin Against Nicotine-induced Damages on Male Mice Liver.Int J Prev Med. 2015 Sep 10;6:92. doi: 10.4103/2008-7802.165203. eCollection 2015. Int J Prev Med. 2015. PMID: 26442615 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin improves liver damage in male mice exposed to nicotine.J Tradit Complement Med. 2015 Jan 31;6(2):176-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.11.034. eCollection 2016 Apr. J Tradit Complement Med. 2015. PMID: 27114942 Free PMC article.
-
Liver and kidney toxicity in chronic use of opioids: an experimental long term treatment model.J Biosci. 2005 Mar;30(2):245-52. doi: 10.1007/BF02703705. J Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15886461
Cited by
-
Efficiency of Thyme and Oregano Essential Oils in Counteracting the Hazardous Effects of Malathion in Rats.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 28;14(17):2497. doi: 10.3390/ani14172497. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272282 Free PMC article.
-
Thyme and Oregano Oil Potential Therapeutics against Malathion Toxicity through Biochemical, Histological, and Cytochrome P450 1A2 Activities in Male Wistar Rats.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 9;14(19):2914. doi: 10.3390/ani14192914. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409863 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids in natural products for the therapy of liver diseases: progress and future opportunities.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 24;15:1485065. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1485065. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39512816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detoxification technology and mechanism of processing with Angelicae sinensis radix in reducing the hepatotoxicity induced by rhizoma Dioscoreae bulbiferae in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 28;13:984858. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984858. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249801 Free PMC article.
-
Royal jelly protects dichlorvos liver-induced injury in male Wistar rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2022 Jan 15;17(2):209-218. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.335178. eCollection 2022 Apr. Res Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35280838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schuppan D, Jia JD, Brinkhaus B, Hahn EG. Herbal products for liver diseases: A therapeutic challenge for the new millennium. Hepatology. 1999;30:1099–104. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

