Sensory overamplification in layer 5 auditory corticofugal projection neurons following cochlear nerve synaptic damage
- PMID: 29941910
- PMCID: PMC6018400
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04852-y
Sensory overamplification in layer 5 auditory corticofugal projection neurons following cochlear nerve synaptic damage
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Sensory overamplification in layer 5 auditory corticofugal projection neurons following cochlear nerve synaptic damage.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 3;9(1):3158. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05333-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30076289 Free PMC article.
Abstract
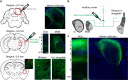
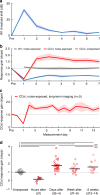
Layer 5 (L5) cortical projection neurons innervate far-ranging brain areas to coordinate integrative sensory processing and adaptive behaviors. Here, we characterize a plasticity in L5 auditory cortex (ACtx) neurons that innervate the inferior colliculus (IC), thalamus, lateral amygdala and striatum. We track daily changes in sound processing using chronic widefield calcium imaging of L5 axon terminals on the dorsal cap of the IC in awake, adult mice. Sound level growth functions at the level of the auditory nerve and corticocollicular axon terminals are both strongly depressed hours after noise-induced damage of cochlear afferent synapses. Corticocollicular response gain rebounded above baseline levels by the following day and remained elevated for several weeks despite a persistent reduction in auditory nerve input. Sustained potentiation of excitatory ACtx projection neurons that innervate multiple limbic and subcortical auditory centers may underlie hyperexcitability and aberrant functional coupling of distributed brain networks in tinnitus and hyperacusis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

