Genome-wide association meta-analysis in 269,867 individuals identifies new genetic and functional links to intelligence
- PMID: 29942086
- PMCID: PMC6411041
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0152-6
Genome-wide association meta-analysis in 269,867 individuals identifies new genetic and functional links to intelligence
Abstract
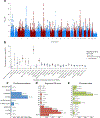
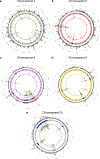
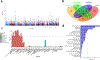
Intelligence is highly heritable1 and a major determinant of human health and well-being2. Recent genome-wide meta-analyses have identified 24 genomic loci linked to variation in intelligence3-7, but much about its genetic underpinnings remains to be discovered. Here, we present a large-scale genetic association study of intelligence (n = 269,867), identifying 205 associated genomic loci (190 new) and 1,016 genes (939 new) via positional mapping, expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) mapping, chromatin interaction mapping, and gene-based association analysis. We find enrichment of genetic effects in conserved and coding regions and associations with 146 nonsynonymous exonic variants. Associated genes are strongly expressed in the brain, specifically in striatal medium spiny neurons and hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Gene set analyses implicate pathways related to nervous system development and synaptic structure. We confirm previous strong genetic correlations with multiple health-related outcomes, and Mendelian randomization analysis results suggest protective effects of intelligence for Alzheimer's disease and ADHD and bidirectional causation with pleiotropic effects for schizophrenia. These results are a major step forward in understanding the neurobiology of cognitive function as well as genetically related neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Financial Interests Statement
PF Sullivan reports the following potentially competing financial interests: Lundbeck (advisory committee), Pfizer (Scientific Advisory Board member), and Roche (grant recipient, speaker reimbursement). G Breen reports consultancy and speaker fees from Eli Lilly and Illumina and grant funding from Eli Lilly. J Hjerling-Leffler reports interests from Cartana (Scientific Advisor) and Roche (grant recipient). TD Cannon is a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and Lundbeck A/S. All other authors declare no financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Methods-Only References
-
- Purcell S, Cherny SS & Sham PC Genetic Power Calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics 19, 149–150 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG049789/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079800/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AA017828/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH098126/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- PL1 MH083271/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085772/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG037985/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- PL1 NS062410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G19/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 MH077807/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH092515/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0600237/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH080912/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033369/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH085812/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085018/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 MH083269/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 DE019580/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M013111/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- L30 MH104879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028555/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008983/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031990/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG045633/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA022537/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH080173/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG008761/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA011408/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA037904/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA023974/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018164/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0100594/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG010175/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 DA024853/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- BB/F022441/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901461/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom

