Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® alleviates neurosensory symptoms in patients with dementia: a meta-analysis of treatment effects on tinnitus and dizziness in randomized, placebo-controlled trials
- PMID: 29942120
- PMCID: PMC6005330
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S157877
Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® alleviates neurosensory symptoms in patients with dementia: a meta-analysis of treatment effects on tinnitus and dizziness in randomized, placebo-controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Tinnitus and dizziness are frequent in old age and often seen as concomitant symptoms in patients with dementia. In earlier clinical trials, Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® was found to alleviate tinnitus and dizziness in elderly patients. Consequently, a meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the effects of EGb 761® at a daily dose of 240 mg on tinnitus and dizziness associated with dementia.
Methods: Randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials of G. biloba extract EGb 761® identified by a systematic database search were included in a meta-analysis if they met all of the following selection criteria: 1) diagnosis of dementia according to generally accepted criteria, 2) treatment period of at least 20 weeks, 3) outcome measures covering at least two of the three conventional domains of assessment, 4) presence and severity of dizziness and tinnitus were assessed, and 5) assessment was done before and after randomized treatment.
Results: Five trials that met the inclusion criteria were included in the meta-analysis. The risk of bias was judged as low, with Jadad scores of 3 and 5. In all trials, 11-point box scales were used to assess the severity of tinnitus and dizziness. Overall, EGb 761® was superior to placebo, with weighted mean differences for change from baseline, calculated in meta-analyses using random effects models, of -1.06 (95% CI: -1.77, -0.36) for tinnitus (p = 0.003) and -0.77 (95% CI: -1.44, -0.09) for dizziness (p = 0.03).
Conclusion: Our findings support the notion that EGb 761® is also effective in alleviating concomitant neurosensory symptoms in patients with dementia.
Keywords: gait; hearing; inner ear; neurodegenerative disorders; review; unsteadiness.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure R Maire received a speaker honorarium from Schwabe Pharma AG, Kuessnacht, Switzerland; R Kalla and G Mantokoudis were supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grant #320030-173081); R Ihl received speaker honoraria from Dr Willmar Schwabe GmbH & Co. KG, Karlsruhe, Germany; H Mueller and R Hoerr are full-time employees of Dr Willmar Schwabe GmbH & Co. KG receiving fixed salaries. R Spiegel reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
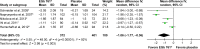

References
-
- Gopinath B, McMahon CM, Rochtchina E, Karpa MJ, Mitchell P. Incidence, persistence, and progression of tinnitus symptoms in older adults: the Blue Mountains Hearing Study. Ear Hear. 2010;31:407–412. - PubMed
-
- McCormack A, Edmondson-Jones M, Somerset S, Hall D. A systematic review of the reporting of tinnitus prevalence and severity. Hear Res. 2016;337:70–79. - PubMed
-
- Schneider LS, DeKosky ST, Farlow MR, Tariot PN, Hoerr R, Kieser M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of two doses of Ginkgo biloba extract in dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005;2:541–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

