Effectiveness of nifedipine in threatened preterm labor: a randomized trial
- PMID: 29942162
- PMCID: PMC6007202
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S159062
Effectiveness of nifedipine in threatened preterm labor: a randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: Threatened preterm labor is a condition in which regular uterine contractions occur at least 1 time in 10 minutes and persist for more than 30 minutes before completion of 37 weeks of gestation without dilatation of the cervix. In preterm labor with cervical dilatation, the efficacy of tocolytics was proven for prolonging pregnancy. However, in threatened preterm labor, the efficacy of tocolytics has not yet been well studied. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of nifedipine versus a placebo for inhibiting uterine contraction in threatened preterm labor.
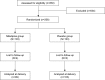
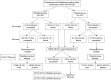
Materials and methods: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study with 206 threatened preterm labor patients was undertaken. The participants were randomly allocated into either nifedipine or placebo groups. The proportion of patients with successful treatment, gestational age at delivery, and neonatal outcome were compared between the 2 groups.
Results: After 90 minutes of treatment, 88.3% of the nifedipine group and 69.9% of the placebo group had no uterine contraction (P<0.001). Nifedipine led to successful treatment outcomes in 77.6% of the total participants compared with 49.5% in the placebo group (P<0.001). The remainder of the participants from both groups needed a second-line tocolytic drug. Of these, 9.7% in the nifedipine group delivered within 48 hours compared with 12.6% in the placebo group (P>0.05). Mean gestation age at delivery and neonatal complications for both groups were not significantly different.
Conclusion: Nifedipine had a higher success rate for inhibiting threatened preterm contractions.
Keywords: nifedipine; preterm labor; randomized trial; threatened preterm labor; tocolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Chawanpaiboon S, Pimol K, Sirisomboon R. Comparison of success rate of nifedipine, progesterone, and bed rest for inhibiting uterine contraction in threatened preterm labor. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011;37(7):787–791. - PubMed
-
- Chawanpaiboon S, Sutantawibul A, Pimol K, Sirisomboon R, Worapitaksanond S. Preliminary study: comparison of the efficacy of progesterone and nifedipine in inhibiting threatened preterm labour in Siriraj Hospital. Thai J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;17(1):23–29.
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet. 2015;385(9966):430–440. - PubMed
-
- Bhutta ZA, Das JK, Bahl R, et al. Can available interventions end preventable deaths in mothers, newborn babies, and stillbirths, and at what cost? Lancet. 2014;384(9940):347–370. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources