Empirical antimicrobial treatment in haemato-/oncological patients with neutropenic sepsis
- PMID: 29942661
- PMCID: PMC6012562
- DOI: 10.1136/esmoopen-2018-000348
Empirical antimicrobial treatment in haemato-/oncological patients with neutropenic sepsis
Abstract
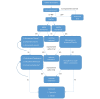
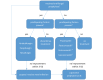
Neutropenic sepsis in haemato-/oncological patients is a medical emergency, as infections may show a fulminant clinical course. Early differentiation between sepsis and febrile neutropenic response often proves to be challenging. To assess the severity of the illness, different tools, which are discussed in this article, are available. Once the diagnosis has been established, the correct use of early empirical antibiotic and antifungal treatment is key in improving patient survival. Therefore, profound knowledge of local resistance patterns is mandatory and carefully designed antibiotic regimens have to be established in cooperation with local microbiologists or infectious diseases specialists. In the following, identification, therapy and management of high-risk, neutropenic patients will be reviewed based on experimental and clinical studies, guidelines and reviews.
Keywords: anti-infective agents; antimicrobial resistance; fever; neutropenia; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can mortality of cancer patients with fever and neutropenia be improved?Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;28(6):505-13. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000202. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26374951 Review.
-
Management of febrile neutropenia in the perspective of antimicrobial de-escalation and discontinuation.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2019 Dec;17(12):983-995. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2019.1573670. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2019. PMID: 30686067 Review.
-
New guidelines for the clinical management of febrile neutropenia and sepsis in pediatric oncology patients.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2007 May;83(2 Suppl):S54-63. doi: 10.2223/JPED.1624. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2007. PMID: 17530138 Review.
-
Diagnosis and empirical treatment of fever of unknown origin (FUO) in adult neutropenic patients: guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (DGHO).Ann Hematol. 2017 Nov;96(11):1775-1792. doi: 10.1007/s00277-017-3098-3. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Ann Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28856437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial prophylaxis and outpatient management of fever and neutropenia in adults treated for malignancy: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Feb 20;31(6):794-810. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.8661. Epub 2013 Jan 14. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23319691
Cited by
-
Container closure integrity testing and process validation of closed system transfer devices for aseptic reconstitution of drug vials connected to fluid bags.Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2024 Jun 21;31(4):358-362. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2022-003604. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2024. PMID: 36792349 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of empirical antifungal treatment on mortality in non-neutropenic critically ill patients: a propensity-matched retrospective cohort study.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Dec;41(12):1421-1432. doi: 10.1007/s10096-022-04507-3. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36255537
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

