SNARE Complex-Associated Proteins in the Lateral Amygdala of Macaca mulatta Following Long-Term Ethanol Drinking
- PMID: 29944190
- PMCID: PMC6120765
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13821
SNARE Complex-Associated Proteins in the Lateral Amygdala of Macaca mulatta Following Long-Term Ethanol Drinking
Abstract
Background: Recent work with long-term ethanol (EtOH) self-administration in nonhuman primate models has revealed a complex array of behavioral and physiological effects that closely mimic human alcohol abuse. Detailed neurophysiological analysis in these models suggests a myriad of pre- and postsynaptic neurobiological effects that may contribute to the behavioral manifestations of long-term EtOH drinking. The molecular mechanisms regulating presynaptic effects of this chronic EtOH exposure are largely unknown. To this end, we analyzed the effects of long-term EtOH self-administration on the levels of presynaptic SNARE complex proteins in Macaca mulatta basolateral amygdala, a brain region known to regulate both aversive and reward-seeking behaviors.
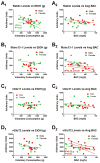
Methods: Basolateral amygdala samples from control and EtOH-drinking male and female monkeys were processed. Total basolateral amygdala protein was analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies directed against both core SNARE and SNARE-associated proteins. We also performed correlational analyses between protein expression levels and a number of EtOH drinking parameters, including lifetime grams of EtOH consumed, preference, and blood alcohol concentration.
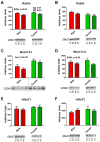
Results: Significant interactions or main effects of sex/drinking were seen for a number of SNARE core and SNARE-associated proteins. Across the range of EtOH-drinking phenotypes, SNAP25 and Munc13-1 proteins levels were significantly different between males and females, and Munc13-2 levels were significantly lower in animals with a history of EtOH drinking. A separate analysis of very heavy-drinking individuals revealed significant decreases in Rab3c (females) and complexin 2 (males).
Conclusions: Protein expression analysis of basolateral amygdala total protein from controls and animals following long-term EtOH self-administration suggests a number of alterations in core SNARE or SNARE-associated components that could dramatically alter presynaptic function. A number of proteins or multiprotein components were also correlated with EtOH drinking behavior, which suggest a potentially heritable role for presynaptic SNARE proteins.
Keywords: Complexin 1/2; Macaque; Munc13-1/2; Munc18-1; Rab3a/c.
© 2018 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SNARE Complex-Associated Proteins and Alcohol.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Jan;44(1):7-18. doi: 10.1111/acer.14238. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 31724225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strain-Dependent Effects of Acute Alcohol on Synaptic Vesicle Recycling and Post-Tetanic Potentiation in Medial Glutamate Inputs to the Mouse Basolateral Amygdala.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017 Apr;41(4):735-746. doi: 10.1111/acer.13343. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 28118494 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic alcohol self-administration in monkeys shows long-term quantity/frequency categorical stability.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Nov;38(11):2835-43. doi: 10.1111/acer.12547. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 25421519 Free PMC article.
-
Protein expression changes in the nucleus accumbens and amygdala of inbred alcohol-preferring rats given either continuous or scheduled access to ethanol.Alcohol. 2006 Aug;40(1):3-17. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2006.10.001. Alcohol. 2006. PMID: 17157716
-
Role of the Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid Receptor System in the Motivational Effects of Ethanol.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017 Aug;41(8):1402-1418. doi: 10.1111/acer.13406. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2017. PMID: 28425121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of G protein-coupled receptor-associated proteins in the caudate and the putamen of cynomolgus macaques following chronic ethanol drinking.J Neurochem. 2024 Sep;168(9):2722-2735. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16134. Epub 2024 May 23. J Neurochem. 2024. PMID: 38783749 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression of Presynaptic Munc13-1 and Munc13-2 in Mouse Hippocampus Following Ethanol Drinking.Neuroscience. 2022 Apr 1;487:166-183. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.02.008. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35167938 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Effects Induced by Alcohol.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023 Feb 11:10.1007/7854_2022_412. doi: 10.1007/7854_2022_412. Online ahead of print. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36765015 Free PMC article.
-
SNARE Complex-Associated Proteins and Alcohol.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Jan;44(1):7-18. doi: 10.1111/acer.14238. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 31724225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor-1 Neurons in the Lateral Amygdala Display Selective Sensitivity to Acute and Chronic Ethanol Exposure.eNeuro. 2020 Mar 5;7(2):ENEURO.0420-19.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0420-19.2020. Print 2020 Mar/Apr. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32041742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander GM, Graef JD, Hammarback JA, Nordskog BK, Burnett EJ, Daunais JB, Bennett AJ, Friedman DP, Suomi SJ, Godwin DW. Disruptions in serotonergic regulation of cortical glutamate release in primate insular cortex in response to chronic ethanol and nursery rearing. Neuroscience. 2012;207:167–81. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

