Microwave radiation alters burn injury-evoked electric potential in Nicotiana benthamiana
- PMID: 29944441
- PMCID: PMC6110360
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1486145
Microwave radiation alters burn injury-evoked electric potential in Nicotiana benthamiana
Abstract
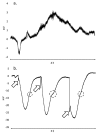
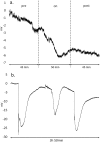
The dielectric effect enforced on charged ions and dipolar molecules by the oscillating electric field of microwaves may influence electric signaling in plants. In the present study, the exposure of Nicotiana benthamiana plants to continuous wave 2.45 GHz microwave radiation with 1.9 - 2.1 W m-2 power density significantly reduced the amplitude of leaf burning-induced variation potential along the plant stem. The change in amplitude of the variation potential occurred mainly because of a significant reduction of the depolarization rate. This effect was not observed during the post-microwave exposure period. The unique characteristics observed in the variation potentials were also observed under microwave exposure, suggesting unaffected information delivery to distant locations or unaffected transport of specific chemicals generated by the injury.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; electromagnetic radiation; non-thermal effect; plant signaling; wounding.
Figures

References
-
- Pont A, Pujolle G, Raghavan SV. Communications: wireless in developing countries and networks of the future. Springer, 2010, IFIP Advances in information and communication technology, 978-3-642-15475-1. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15476-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
