Diagnostic accuracy of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 29944682
- PMCID: PMC6019099
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199290
Diagnostic accuracy of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is used to detect pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB); however, the diagnostic accuracy of the LAMP assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) is unclear. We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the performance of LAMP in the detection of EPTB.
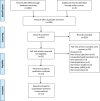
Methods: We searched PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and the Wanfang database for studies published before Sep 16, 2017. We reviewed studies and compared the performance of LAMP with that of a composite reference standard (CRS) and culture for clinically suspected EPTB. We used a bivariate random-effects model to perform meta-analyses and used meta-regression and subgroup analysis to analyze sources of heterogeneity.
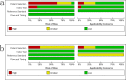
Results: Fourteen articles including 24 independent studies (16 compared LAMP to CRS, 8 to culture) of EPTB were identified. LAMP showed a pooled sensitivity of 77% (95% confidence interval (CI) 68-85), specificity of 99% (95% CI 96-100), and area under SROC curves (AUC) of 0.96 (95% CI 0.94-0.97) against CRS. It showed a pooled sensitivity of 93% (95% CI 88-96), specificity of 77% (95% CI 64-86), and AUC of 0.94 (95% CI 0.92-0.96) against culture. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and AUC of MPB64 LAMP were 86% (95% CI 86-86), 100% (95% CI 100-100), and 0.97 (95% CI 0.95-0.98), respectively, and those of IS6110 LAMP were 75% (95% CI 64-84), 99% (95% CI 90-100), and 0.91 (95% CI 0.88-0.93), respectively, compared with CRS.
Conclusions: These results suggest good diagnostic efficacy of LAMP in the detection of EPTB. Additionally, the diagnostic efficacy of MPB64 LAMP was superior to that of IS6110 LAMP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report. 2016.
-
- Norbis L, Alagna R, Tortoli E, Codecasa LR, Migliori GB, Cirillo DM. Challenges and perspectives in the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014;12:633–47. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2014.899900 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aryan E, Makvandi M, Farajzadeh A, Huygen KA, Bifani P, Mousavi SL, et al. A novel and more sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay targeting IS6110 for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Microbiol Res. 2010;165:211–20. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2009.05.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leeflang MM. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20:105–13. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12474 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6: e1000097 doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

