Toward predictive R-loop computational biology: genome-scale prediction of R-loops reveals their association with complex promoter structures, G-quadruplexes and transcriptionally active enhancers
- PMID: 29945198
- PMCID: PMC6125637
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky554
Toward predictive R-loop computational biology: genome-scale prediction of R-loops reveals their association with complex promoter structures, G-quadruplexes and transcriptionally active enhancers
Erratum in
-
Toward predictive R-loop computational biology: genome-scale prediction of R-loops reveals their association with complex promoter structures, G-quadruplexes and transcriptionally active enhancers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 6;46(15):8023. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky690. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30053183 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
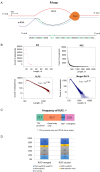
R-loops are three-stranded RNA:DNA hybrid structures essential for many normal and pathobiological processes. Previously, we generated a quantitative R-loop forming sequence (RLFS) model, quantitative model of R-loop-forming sequences (QmRLFS) and predicted ∼660 000 RLFSs; most of them located in genes and gene-flanking regions, G-rich regions and disease-associated genomic loci in the human genome. Here, we conducted a comprehensive comparative analysis of these RLFSs using experimental data and demonstrated the high performance of QmRLFS predictions on the nucleotide and genome scales. The preferential co-localization of RLFS with promoters, U1 splice sites, gene ends, enhancers and non-B DNA structures, such as G-quadruplexes, provides evidence for the mechanical linkage between DNA tertiary structures, transcription initiation and R-loops in critical regulatory genome regions. We introduced and characterized an abundant class of reverse-forward RLFS clusters highly enriched in non-B DNA structures, which localized to promoters, gene ends and enhancers. The RLFS co-localization with promoters and transcriptionally active enhancers suggested new models for in cis and in trans regulation by RNA:DNA hybrids of transcription initiation and formation of 3D-chromatin loops. Overall, this study provides a rationale for the discovery and characterization of the non-B DNA regulatory structures involved in the formation of the RNA:DNA interactome as the basis for an emerging quantitative R-loop biology and pathobiology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
QmRLFS-finder: a model, web server and stand-alone tool for prediction and analysis of R-loop forming sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W527-34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv344. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25883153 Free PMC article.
-
R-loopDB: a database for R-loop forming sequences (RLFS) and R-loops.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D119-D127. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1054. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899586 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalent, Dynamic, and Conserved R-Loop Structures Associate with Specific Epigenomic Signatures in Mammals.Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 7;63(1):167-78. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.032. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27373332 Free PMC article.
-
Intertwining roles of R-loops and G-quadruplexes in DNA repair, transcription and genome organization.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Jul;26(7):1025-1036. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01437-4. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38914786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-quadruplex-R-loop interactions and the mechanism of anticancer G-quadruplex binders.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Dec 2;48(21):11942-11957. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa944. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33137181 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling human pathogenic repeat expansion regions by synergistic and multi-level impacts on molecular connections.Hum Genet. 2023 Feb;142(2):245-274. doi: 10.1007/s00439-022-02500-6. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 36344696 Free PMC article.
-
The extruded non-template strand determines the architecture of R-loops.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 26;47(13):6783-6795. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz341. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31066439 Free PMC article.
-
Properties and biological impact of RNA G-quadruplexes: from order to turmoil and back.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Dec 16;48(22):12534-12555. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1126. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 33264409 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Atypical Nucleic Acids Structures in DNA Double Strand Break Repair: A Tale of R-loops and G-Quadruplexes.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 8;12:742434. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.742434. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34691154 Free PMC article.
-
From R-Loops to G-Quadruplexes: Emerging New Threats for the Replication Fork.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041506. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- White R.L., Hogness D.S.. R loop mapping of the 18S and 28S sequences in the long and short repeating units of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977; 10:177–192. - PubMed
-
- Ratmeyer L., Vinayak R., Zhong Y.Y., Zon G., Wilson W.D.. Sequence specific thermodynamic and structural properties for DNA.RNA Duplexes. Biochemistry. 1994; 33:5298–5304. - PubMed
-
- Drolet M., Phoenix P., Menzel R., Masse E., Liu L.F., Crouch R.J.. Overexpression of RNase H partially complements the growth defect of an Escherichia coli delta topA mutant: R-loop formation is a major problem in the absence of DNA topoisomerase I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1995; 92:3526–3530. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Massé E., Drolet M.. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I inhibits R-loop formation by relaxing transcription-induced negative supercoiling. J. Biol. Chem. 1999; 274:16659–16664. - PubMed
-
- Broccoli S., Rallu F., Sanscartier P., Cerritelli S.M., Crouch R.J., Drolet M.. Effects of RNA polymerase modifications on transcription-induced negative supercoiling and associated R-loop formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2004; 52:1769–1779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

