EWS-FLI1 regulates a transcriptional program in cooperation with Foxq1 in mouse Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 29945296
- PMCID: PMC6125457
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13710
EWS-FLI1 regulates a transcriptional program in cooperation with Foxq1 in mouse Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
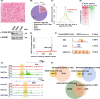
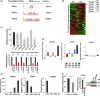
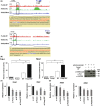
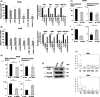
EWS-FLI1 constitutes an oncogenic transcription factor that plays key roles in Ewing sarcoma development and maintenance. We have recently succeeded in generating an ex vivo mouse model for Ewing sarcoma by introducing EWS-FLI1 into embryonic osteochondrogenic progenitors. The model well recapitulates the biological characteristics, small round cell morphology, and gene expression profiles of human Ewing sarcoma. Here, we clarified the global DNA binding properties of EWS-FLI1 in mouse Ewing sarcoma. GGAA microsatellites were found to serve as binding sites of EWS-FLI1 albeit with less frequency than that in human Ewing sarcoma; moreover, genomic distribution was not conserved between human and mouse. Nevertheless, EWS-FLI1 binding sites within GGAA microsatellites were frequently associated with the histone H3K27Ac enhancer mark, suggesting that EWS-FLI1 could affect global gene expression by binding its target sites. In particular, the Fox transcription factor binding motif was frequently observed within EWS-FLI1 peaks and Foxq1 was identified as the cooperative partner that interacts with the EWS portion of EWS-FLI1. Trib1 and Nrg1 were demonstrated as target genes that are co-regulated by EWS-FLI1 and Foxq1, and are important for cell proliferation and survival of Ewing sarcoma. Collectively, our findings present novel aspects of EWS-FLI1 function as well as the importance of GGAA microsatellites.
Keywords: EWS-FLI1; Ewing sarcoma; Foxq1; GGAA microsatellite; Trib1.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-throughput RNAi screen in Ewing sarcoma cells identifies leucine rich repeats and WD repeat domain containing 1 (LRWD1) as a regulator of EWS-FLI1 driven cell viability.Gene. 2017 Jan 5;596:137-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.10.021. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Gene. 2017. PMID: 27760381
-
Suppression of FOXO1 is responsible for a growth regulatory repressive transcriptional sub-signature of EWS-FLI1 in Ewing sarcoma.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 24;33(30):3927-38. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.361. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23995784 Free PMC article.
-
A polypeptide from the junction region sequence of EWS-FLI1 inhibits Ewing's sarcoma cells, interacts with the EWS-FLI1 and partner proteins.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 3;7(1):7172. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07482-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28775288 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of Ewing sarcoma: new therapeutic and transcriptional targets.Annu Rev Pathol. 2012;7:145-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130237. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Annu Rev Pathol. 2012. PMID: 21942527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blocking the road, stopping the engine or killing the driver? Advances in targeting EWS/FLI-1 fusion in Ewing sarcoma as novel therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Nov;18(11):1315-28. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.947963. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 25162919 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical In Vivo Modeling of Pediatric Sarcoma-Promises and Limitations.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 8;10(8):1578. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081578. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33918045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Forkhead Box Family in Bone Metabolism and Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 28;12:772237. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.772237. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35153742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of EWSR1-FLI1 Function by Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;15(2):382. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020382. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anatomic Origin of Osteochondrogenic Progenitors Impacts Sensitivity to EWS-FLI1-Induced Transformation.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Mar 6;11(3):313. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030313. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30845695 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in modeling EWS-FLI1-driven transgenic mouse model for Ewing sarcoma.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):12181-12194. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34956445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gaspar N, Hawkins DS, Dirksen U, et al. Ewing sarcoma: current management and future approaches through collaboration. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3036‐3046. - PubMed
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA‐binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992;359:162‐165. - PubMed
-
- Riggi N, Suva ML, Suva D, et al. EWS‐FLI‐1 expression triggers a Ewing's sarcoma initiation program in primary human mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2176‐2185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

