Inhibition of MicroRNA-155 Supports Endothelial Tight Junction Integrity Following Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation
- PMID: 29945912
- PMCID: PMC6064884
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009244
Inhibition of MicroRNA-155 Supports Endothelial Tight Junction Integrity Following Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation
Abstract
Background: Brain microvascular endothelial cells form a highly selective blood brain barrier regulated by the endothelial tight junctions. Cerebral ischemia selectively targets tight junction protein complexes, which leads to significant damage to cerebral microvasculature. Short noncoding molecules called microRNAs are implicated in the regulation of various pathological states, including endothelial barrier dysfunction. In the present study, we investigated the influence of microRNA-155 (miR-155) on the barrier characteristics of human primary brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs).
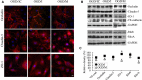
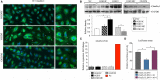
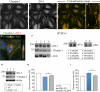
Methods and results: Oxygen-glucose deprivation was used as an in vitro model of ischemic stroke. HBMECs were subjected to 3 hours of oxygen-glucose deprivation, followed by transfections with miR-155 inhibitor, mimic, or appropriate control oligonucleotides. Intact normoxia control HBMECs and 4 oxygen-glucose deprivation-treated groups of cells transfected with appropriate nucleotide were subjected to endothelial monolayer electrical resistance and permeability assays, cell viability assay, assessment of NO and human cytokine/chemokine release, immunofluorescence microscopy, Western blot, and polymerase chain reaction analyses. Assessment of endothelial resistance and permeability demonstrated that miR-155 inhibition improved HBMECs monolayer integrity. In addition, miR-155 inhibition significantly increased the levels of major tight junction proteins claudin-1 and zonula occludens protein-1, while its overexpression reduced these levels. Immunoprecipitation and colocalization analyses detected that miR-155 inhibition supported the association between zonula occludens protein-1 and claudin-1 and their stabilization at the HBMEC membrane. Luciferase reporter assay verified that claudin-1 is directly targeted by miR-155.
Conclusions: Based on these results, we conclude that miR-155 inhibition-induced strengthening of endothelial tight junctions after oxygen-glucose deprivation is mediated via its direct target protein claudin-1.
Keywords: brain microvascular endothelial cells; endothelial barrier; microRNA; oxygen‐glucose deprivation; tight junctions.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-Induced MicroRNA-212/132 Alter Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity Through Inhibition of Tight Junction-Associated Proteins in Human and Mouse Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Transl Stroke Res. 2019 Dec;10(6):672-683. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0683-2. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Transl Stroke Res. 2019. PMID: 30617994 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-derived triterpene celastrol ameliorates oxygen glucose deprivation-induced disruption of endothelial barrier assembly via inducing tight junction proteins.Phytomedicine. 2016 Dec 1;23(13):1621-1628. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27823626
-
Baicalin reduces the permeability of the blood-brain barrier during hypoxia in vitro by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jun 1;141(2):714-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.063. Epub 2011 Sep 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21920425
-
Site-specific m6A-miR-494-3p, not unmethylated miR-494-3p, compromises blood brain barrier by targeting tight junction protein 1 in intracranial atherosclerosis.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep;182(18):4221-4235. doi: 10.1111/bph.17374. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39419283 Review.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of Endothelial Junction Proteins and Clinical Consequence.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5078627. doi: 10.1155/2016/5078627. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27999452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in central nervous system diseases: A prospective role in regulating blood-brain barrier integrity.Exp Neurol. 2020 Jan;323:113094. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113094. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31676317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsa_circ_0060927 participates in the regulation of Caudatin on colorectal cancer malignant progression by sponging miR-421/miR-195-5p.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 May;36(5):e24393. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24393. Epub 2022 Apr 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35373390 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Unraveling the Hidden Players in Disease Pathogenesis.Cells. 2024 Jun 19;13(12):1063. doi: 10.3390/cells13121063. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38920691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ_0000370 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the miR-502-5p/SIRT1 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2024 Apr;62(2):1231-1247. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10468-9. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37561331
-
miR-155 as an Important Regulator of Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4332. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094332. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M. The blood‐brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 2004;16:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Haseloff RF, Dithmer S, Winkler L, Wolburg H, Blasig IE. Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at the blood‐brain barrier: structural and functional aspects. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;38:16–25. - PubMed
-
- Krause G, Winkler L, Mueller SL, Haseloff RF, Piontek J, Blasig IE. Structure and function of claudins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:631–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

