Cereblon modulator iberdomide induces degradation of the transcription factors Ikaros and Aiolos: immunomodulation in healthy volunteers and relevance to systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 29945920
- PMCID: PMC6161670
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212916
Cereblon modulator iberdomide induces degradation of the transcription factors Ikaros and Aiolos: immunomodulation in healthy volunteers and relevance to systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objectives: IKZF1 and IKZF3 (encoding transcription factors Ikaros and Aiolos) are susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The pharmacology of iberdomide (CC-220), a cereblon (CRBN) modulator targeting Ikaros and Aiolos, was studied in SLE patient cells and in a phase 1 healthy volunteer study.
Methods: CRBN, IKZF1 and IKZF3 gene expression was measured in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients with SLE and healthy volunteers. Ikaros and Aiolos protein levels were measured by Western blot and flow cytometry. Anti-dsDNA and anti-phospholipid autoantibodies were measured in SLE PBMC cultures treated for 7 days with iberdomide. Fifty-six healthy volunteers were randomised to a single dose of iberdomide (0.03-6 mg, n=6 across seven cohorts) or placebo (n=2/cohort). CD19+ B cells, CD3+ T cells and intracellular Aiolos were measured by flow cytometry. Interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-1β production was stimulated with anti-CD3 and lipopolysaccharide, respectively, in an ex vivo whole blood assay.
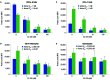
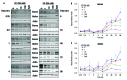
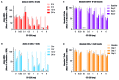
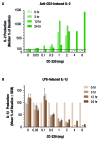
Results: SLE patient PBMCs expressed significantly higher CRBN (1.5-fold), IKZF1 (2.1-fold) and IKZF3 (4.1-fold) mRNA levels compared with healthy volunteers. Iberdomide significantly reduced Ikaros and Aiolos protein levels in B cells, T cells and monocytes. In SLE PBMC cultures, iberdomide inhibited anti-dsDNA and anti-phospholipid autoantibody production (IC50 ≈10 nM). Single doses of iberdomide (0.3-6 mg) in healthy volunteers decreased intracellular Aiolos (minimum mean per cent of baseline: ≈12%-28% (B cells); ≈0%-33% (T cells)), decreased absolute CD19+ B cells, increased IL-2 and decreased IL-1β production ex vivo.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate pharmacodynamic activity of iberdomide and support its further clinical development for the treatment of SLE.
Trial registration number: NCT01733875; Results.
Keywords: B cells; autoantibodies; autoimmunity; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors either are, or have been, employees and shareholders of Celgene.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phase 2 Trial of Iberdomide in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.N Engl J Med. 2022 Mar 17;386(11):1034-1045. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2106535. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 35294813 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of targeting the transcription factors Ikaros and Aiolos on B cell activation and differentiation in systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus Sci Med. 2021 Mar;8(1):e000445. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2020-000445. Lupus Sci Med. 2021. PMID: 33727237 Free PMC article.
-
Aiolos Overexpression in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus B Cell Subtypes and BAFF-Induced Memory B Cell Differentiation Are Reduced by CC-220 Modulation of Cereblon Activity.J Immunol. 2017 Oct 1;199(7):2388-2407. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601725. Epub 2017 Aug 28. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28848067 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Ikaros and Aiolos: reviewing novel protein degraders for the treatment of multiple myeloma, with a focus on iberdomide and mezigdomide.Expert Rev Hematol. 2024 Aug;17(8):445-465. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2024.2382897. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Expert Rev Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39054911 Review.
-
[Cereblon as a primary target of IMiDs].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2019;60(9):1013-1019. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.60.1013. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2019. PMID: 31597822 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
De-Novo Design of Cereblon (CRBN) Effectors Guided by Natural Hydrolysis Products of Thalidomide Derivatives.J Med Chem. 2019 Jul 25;62(14):6615-6629. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00454. Epub 2019 Jul 12. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31251063 Free PMC article.
-
Novel immunomodulatory drugs and neo-substrates.Biomark Res. 2020 Jan 9;8:2. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-0182-y. eCollection 2020. Biomark Res. 2020. PMID: 31938543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of activated T cell survival in rheumatic autoimmune diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Apr;18(4):232-244. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00741-9. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35075294 Review.
-
Potential T Cell-Intrinsic Regulatory Roles for IRF5 via Cytokine Modulation in T Helper Subset Differentiation and Function.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 3;11:1143. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01143. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Gene CDC27 Causes SLE and Is Associated With the Disease Activity.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 28;13:876963. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.876963. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35418986 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

