Routes of phosphoryl group transfer during signal transmission and signal decay in the dimeric sensor histidine kinase ArcB
- PMID: 29945971
- PMCID: PMC6109937
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003910
Routes of phosphoryl group transfer during signal transmission and signal decay in the dimeric sensor histidine kinase ArcB
Abstract
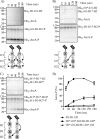
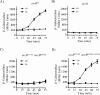
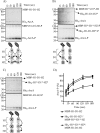
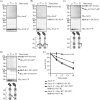
The Arc (anoxic redox control) two-component system of Escherichia coli, comprising ArcA as the response regulator and ArcB as the sensor histidine kinase, modulates the expression of numerous genes in response to respiratory growth conditions. Under reducing growth conditions, ArcB autophosphorylates at the expense of ATP, and transphosphorylates ArcA via a His292 → Asp576 → His717 → Asp54 phosphorelay, whereas under oxidizing growth conditions, ArcB catalyzes the dephosphorylation of ArcA-P by a reverse Asp54 → His717 → Asp576 → Pi phosphorelay. However, the exact phosphoryl group transfer routes and the molecular mechanisms determining their directions are unclear. Here, we show that, during signal propagation, the His292 → Asp576 and Asp576 → His717 phosphoryl group transfers within ArcB dimers occur intra- and intermolecularly, respectively. Moreover, we report that, during signal decay, the phosphoryl group transfer from His717 to Asp576 takes place intramolecularly. In conclusion, we present a mechanism that dictates the direction of the phosphoryl group transfer within ArcB dimers and that enables the discrimination of the kinase and phosphatase activities of ArcB.
Keywords: ArcB/A two-component system; bacteria; bacterial signal transduction; conformation; histidine kinase; intermolecular phosphotransfer; intramolecular phosphotransfer; phosphorelay; phosphoryl transfer; phosphorylation; sensor kinase.
© 2018 Teran-Melo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


References
-
- Jung W. S., Jung Y. R., Oh D. B., Kang H. A., Lee S. Y., Chavez-Canales M., Georgellis D., and Kwon O. (2008) Characterization of the Arc two-component signal transduction system of the capnophilic rumen bacterium Mannheimia succiniciproducens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 284, 109–119 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01187.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lynch A. S., and Lin E. C. (1996) Regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. in Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology (Neidhardt F. C., Curtis R., Ingraham A. L., Lin E. C. C., Low K. B., Magasanik B., Reznikoff W. S., Riley M., Schaechter M., and Umbarger H. E., eds) pp. 1526–1538, American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

