Protein phosphatase 2A stimulates activation of TFEB and TFE3 transcription factors in response to oxidative stress
- PMID: 29945972
- PMCID: PMC6093222
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003471
Protein phosphatase 2A stimulates activation of TFEB and TFE3 transcription factors in response to oxidative stress
Abstract
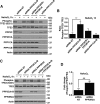
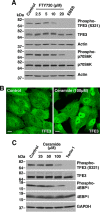
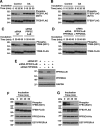
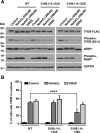
Adaptations and responses to stress conditions are fundamental processes that all cells must accomplish to maintain or restore cellular homeostasis. Cells have a plethora of response pathways to mitigate the effect of different environmental stressors. The transcriptional regulators transcription factor EB (TFEB) and transcription factor binding to IGHM enhancer 3 (TFE3) play a key role in the control of these stress pathways. Therefore, understanding their regulation under different stress conditions is of great interest. Here, using a range of human and murine cells, we show that TFEB and TFE3 are activated upon induction of acute oxidative stress by sodium arsenite via an mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1)-independent process. We found that the mechanism of arsenite-stimulated TFEB and TFE3 activation instead involves protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A)-mediated dephosphorylation at Ser-211 and Ser-321, respectively. Depletion of either the catalytic (PPP2CA+B) or regulatory (PPP2R2A/B55α) subunits of PP2A, as well as PP2A inactivation with the specific inhibitor okadaic acid, abolished TFEB and TFE3 activation in response to sodium arsenite. Conversely, PP2A activation by ceramide or the sphingosine-like compound FTY720 was sufficient to induce TFE3 nuclear translocation. MS analysis revealed that PP2A dephosphorylates TFEB at several residues, including Ser-109, Ser-114, Ser-122, and Ser-211, thus facilitating TFEB activation. Overall, this work identifies a critical mechanism that activates TFEB and TFE3 without turning off mTORC1 activity. We propose that this mechanism may enable some cell types such as immune or cancer cells that require simultaneous TFEB/TFE3 and mTORC1 signaling to survive and achieve robust cell growth in stressful environments.
Keywords: mTORC1; nuclear translocation; okadaic acid; oxidative stress; phosphatase; protein phosphatase 2 (PP2A); sodium arsenite; transcription factor; transcription factor EB; transcription factor binding to IGHM enhancer 3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



References
-
- Sardiello M., Palmieri M., di Ronza A., Medina D. L., Valenza M., Gennarino V. A., Di Malta C., Donaudy F., Embrione V., Polishchuk R. S., Banfi S., Parenti G., Cattaneo E., and Ballabio A. (2009) A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science 325, 473–477 10.1126/science.1174447 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

