Long-Term In Vitro Culture of the Syphilis Spirochete Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum
- PMID: 29946052
- PMCID: PMC6020297
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01153-18
Long-Term In Vitro Culture of the Syphilis Spirochete Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum
Abstract
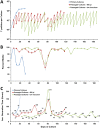
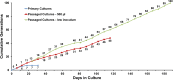
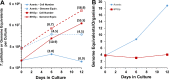
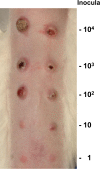
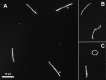
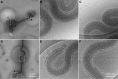
Investigation of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum, the spirochete that causes syphilis, has been hindered by an inability to culture the organism continuously in vitro despite more than a century of effort. In this study, long-term logarithmic multiplication of T. pallidum was attained through subculture every 6 to 7 days and periodic feeding using a modified medium (T. pallidum culture medium 2 [TpCM-2]) with a previously described microaerobic, rabbit epithelial cell coincubation system. Currently, cultures have maintained continuous growth for over 6 months with full retention of viability as measured by motility and rabbit infectivity. This system has been applied successfully to the well-studied Nichols strain of T. pallidum, as well as to two recent syphilis isolates, UW231B and UW249B. Light microscopy and cryo-electron microscopy showed that in vitro-cultured T. pallidum retains wild-type morphology. Further refinement of this long-term subculture system is expected to facilitate study of the physiological, genetic, pathological, immunologic, and antimicrobial susceptibility properties of T. pallidum subsp. pallidum and closely related pathogenic Treponema species and subspecies.IMPORTANCE Syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease with a global distribution, is caused by a spiral-shaped bacterium called Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum Previously, T. pallidum was one of the few major bacterial pathogens that had not been cultured long-term in vitro (in a test tube), greatly hindering efforts to better understand this organism and the disease that it causes. In this article, we report the successful long-term cultivation of T. pallidum in a tissue culture system, a finding that is likely to enhance our ability to obtain new information applicable to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of syphilis.
Keywords: Treponema pallidum; cell culture; cell structure; electron microscopy; infectivity; physiology; spirochetes.
Copyright © 2018 Edmondson et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
New Tools for Syphilis Research.mBio. 2018 Jul 31;9(4):e01417-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01417-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30065094 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Parameters Affecting Continuous In Vitro Culture of Treponema pallidum Strains.mBio. 2021 Feb 23;12(1):e03536-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03536-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33622721 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence Variation of Rare Outer Membrane Protein β-Barrel Domains in Clinical Strains Provides Insights into the Evolution of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum, the Syphilis Spirochete.mBio. 2018 Jun 12;9(3):e01006-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01006-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29895642 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Cultivation of the Syphilis Spirochete Treponema pallidum.Curr Protoc. 2021 Feb;1(2):e44. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.44. Curr Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33599121 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of the Nichols strain as the type strain of Treponema pallidum.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Feb;75(2):006697. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006697. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40014041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polypeptides of Treponema pallidum: progress toward understanding their structural, functional, and immunologic roles. Treponema Pallidum Polypeptide Research Group.Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):750-79. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.750-779.1993. Microbiol Rev. 1993. PMID: 8246847 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the immune escape mechanism of Treponema pallidum.Infection. 2023 Apr;51(2):305-321. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01939-z. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Infection. 2023. PMID: 36260281 Review.
-
Directly Sequenced Genomes of Contemporary Strains of Syphilis Reveal Recombination-Driven Diversity in Genes Encoding Predicted Surface-Exposed Antigens.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 31;10:1691. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01691. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31417509 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Functional Characterization of Peptides With Antimicrobial Activity From the Syphilis Spirochete, Treponema pallidum.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 3;13:888525. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.888525. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35722306 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of Treponema pallidum Tp0225 reveals an unexpected leucine-rich repeat architecture.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019 Jul 1;75(Pt 7):489-495. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X19007726. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31282868 Free PMC article.
-
Parameters Affecting Continuous In Vitro Culture of Treponema pallidum Strains.mBio. 2021 Feb 23;12(1):e03536-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03536-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33622721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization 2016. Report on global sexually transmitted infection surveillance 2015. WHO Document Production Services, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization 2011. Prevalence and incidence of selected sexually transmitted infections. Methods and results used by WHO to generate 2005 estimates. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44735/9789241502450_eng..... Accessed: 23 May 2018.
-
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, Wijesooriya NS, Unemo M, Low N, Stevens G, Gottlieb S, Kiarie J, Temmerman M. 2015. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 10:e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2016 Disease Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators 2017. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390:1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schaudinn F, Hoffman E. 1905. Vorläufiger Bericht über das Vorkommen für Spirochaeten in syphilitischen Krankheitsprodukten und bei Papillomen. Arb Gesundh AMT Berlin 22:528–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
