Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation
- PMID: 29946135
- PMCID: PMC6205604
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-018-0028-8
Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation
Abstract
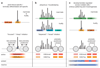
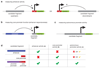
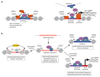
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) core promoters are specialized DNA sequences at transcription start sites of protein-coding and non-coding genes that support the assembly of the transcription machinery and transcription initiation. They enable the highly regulated transcription of genes by selectively integrating regulatory cues from distal enhancers and their associated regulatory proteins. In this Review, we discuss the defining properties of gene core promoters, including their sequence features, chromatin architecture and transcription initiation patterns. We provide an overview of molecular mechanisms underlying the function and regulation of core promoters and their emerging functional diversity, which defines distinct transcription programmes. On the basis of the established properties of gene core promoters, we discuss transcription start sites within enhancers and integrate recent results obtained from dedicated functional assays to propose a functional model of transcription initiation. This model can explain the nature and function of transcription initiation at gene starts and at enhancers and can explain the different roles of core promoters, of Pol II and its associated factors and of the activating cues provided by enhancers and the transcription factors and cofactors they recruit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

