Indirubin, a Constituent of the Chinese Herbal Medicine Qing-Dai, Attenuates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Murine Colitis
- PMID: 29946219
- PMCID: PMC6015798
- DOI: 10.33160/yam.2018.06.005
Indirubin, a Constituent of the Chinese Herbal Medicine Qing-Dai, Attenuates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Murine Colitis
Abstract
Background: Indirubin, a constituent of the Chinese herbal medicine "Qing-Dai," has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy of indirubin for ameliorating colonic inflammation in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease.
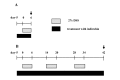
Methods: Mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute and chronic colitis were treated with indirubin in their diet. Clinical and histologic changes were evaluated. In addition, colon levels of interleukin-6, a critical pro-inflammatory mediator, was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
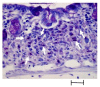
Results: In the model of acute colitis, indirubin treatment improved the loss of body weight. Histology of colonic tissue revealed that indirubin treatment improved the histology grading of colitis (P = 0.02), the extent of submucosal fibrosis (P = 0.018), the number of mucosal toluidine blue-positive cells (P = 0.004) and colon length (P = 0.01). In the model of chronic colitis, indirubin treatment had no significant effect on pathologic findings except for colon length (P = 0.003). However, indirubin administration significantly reduced colon levels of interleukin-6 in the chronic-colitis model (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Our study clearly showed that oral intake of indirubin can improve murine DSS-induced colitis (which mimics human inflammatory bowel disease).
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; DSS-induced colitis model; Qing-Dai; indirubin; inflammatory bowel disease.
Figures






References
-
- Liu XM, Wang LG, Li HY, Ji XJ. Induction of differentiation and down-regulation of c-myb gene expression in ML-1 human myeloblastic leukemia cells by the clinically effective anti-leukemia agent meisoindigo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1996;51:1545-51. - PubMed
-
- Eisenbrand G, Hippe F, Jakobs S, Muehlbeyer S. Molecular mechanisms of indirubin and its derivatives: novel anticancer molecules with their origin in traditional Chinese phytomedicine. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130:627-35. - PubMed
-
- Kunikata T, Tatefuji T, Aga H, Iwaki K, Ikeda M, Kurimoto M. Indirubin inhibits inflammatory reactions in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;410:93-100. - PubMed
-
- Mak NK, Leung CY, Wei XY, Shen XL, Wong RN, Leung KN, et al. Inhibition of RANTES expression by indirubin in influenza virus-infected human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;67:167-74. - PubMed
-
- Kim SA, Kim YC, Kim SW, Lee SH, Min JJ, Ahn SG, et al. Antitumor activity of novel indirubin derivatives in rat tumor model. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:253-9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
