Resolvin E1 Promotes Bone Preservation Under Inflammatory Conditions
- PMID: 29946319
- PMCID: PMC6005849
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01300
Resolvin E1 Promotes Bone Preservation Under Inflammatory Conditions
Abstract
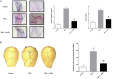
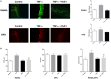
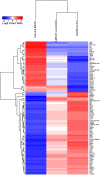
Resolvins are endogenous lipid mediators derived from omega-3 fatty acids. Resolvin E1 (RvE1), derived from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), modulates osteoclasts and immune cells in periodontal disease models. The direct role of RvE1 in bone remodeling is not well understood. The objective of this study was to determine the impact of RvE1 on bone remodeling under inflammatory conditions. Our working hypothesis is that RvE1 downregulates bone resorption through direct actions on both osteoblast and osteoclast function in inflammatory osteoclastogenesis. A tumor necrosis factor-α induced local calvarial osteolysis model with or without the systemic administration of RvE1 was used. To evaluate osteoclastogenesis and NFκB signaling pathway activity, murine bone tissue was evaluated by Micro CT (μCT) analysis, TRAP staining, and immunofluorescence analysis. Mechanistically, to evaluate the direct role of RvE1 impacting bone cells, primary calvarial mouse osteoblasts were stimulated with interleukin (IL)-6 (10 ng/ml) and IL-6 receptor (10 ng/ml) and simultaneously incubated with or without RvE1 (100 nM). Expression of receptor activator of NFκB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) was measured by ELISA. RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) and differential expression analysis was performed to determine signaling pathways impacted by RvE1. The systemic administration of RvE1 reduced calvarial bone resorption as determined by µCT. Histologic analysis of calvaria revealed that osteoclastogenesis was reduced as determined by number and size of osteoclasts in TRAP-stained sections (p < 0.05). Immunofluorescence staining of calvarial sections revealed that RvE1 reduced RANKL secretion by 25% (p < 0.05). Stimulation of osteoblasts with IL-6 increased RANKL production by 30% changing the RANKL/OPG to favor osteoclast activation and bone resorption. The ratio changes were reversed by 100 nM RvE1. RvE1 decreased the production of RANKL maintaining an RANKL/OPG more favorable for bone formation. RNA-Seq and transcriptomic pipeline analysis revealed that RvE1 significantly downregulates osteoclast differentiation mediated by differential regulation of NFκB and PI3K-AKT pathways. RvE1 reduces inflammatory bone resorption. This action is mediated, at least in part, by direct actions on bone cells promoting a favorable RANKL/OPG ratio. Mediators of resolution in innate immunity also directly regulate bone cell gene expression that is modulated by RvE1 through at least 14 specific genes in this mouse model.
Keywords: bone; bone metabolism; inflammatory diseases; resolution; resolvin E1; tissue regeneration.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Resolvin E1 and chemokine-like receptor 1 mediate bone preservation.J Immunol. 2013 Jan 15;190(2):689-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103688. Epub 2012 Dec 14. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23241890 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin E1 Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Resorption by Suppressing IL-17-induced RANKL Expression in Osteoblasts and RANKL-induced Osteoclast Differentiation.Yonago Acta Med. 2018 Mar 28;61(1):8-18. doi: 10.33160/yam.2018.03.002. eCollection 2018 Mar. Yonago Acta Med. 2018. PMID: 29599617 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-talk between osteoclasts and osteoblasts in response to strontium treatment: involvement of osteoprotegerin.Bone. 2011 Dec;49(6):1290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.08.031. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Bone. 2011. PMID: 21925296
-
Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Jan;39(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01162-6. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33079279 Review.
-
The role of polyunsaturated ω-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid-derived resolvin E1 (RvE1) in bone preservation.Crit Rev Immunol. 2014;34(4):347-57. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2014009982. Crit Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24941160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potentials and modulatory mechanisms of fatty acids in bone.Cell Prolif. 2020 Feb;53(2):e12735. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12735. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31797479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host Response Modulation Therapy in the Diabetes Mellitus-Periodontitis Conjuncture: A Narrative Review.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 18;14(8):1728. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081728. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subgingival Microbiome and Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediator Pathway Profiles Are Correlated in Periodontal Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 10;12:691216. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.691216. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177951 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Resolvin E1 (RvE1) Treatment Does Not Ameliorate the Severity of Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) in Mice: A Randomized, Prospective, and Controlled Proof of Concept Study.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Oct 31;2019:5689465. doi: 10.1155/2019/5689465. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31780864 Free PMC article.
-
Polarized Macrophages in Periodontitis: Characteristics, Function, and Molecular Signaling.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 7;12:763334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.763334. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34950140 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomson BM, Mundy GR, Chambers TJ. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta induce osteoblastic cells to stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Immunol (1987) 138(3):775–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

