The effects of probiotic supplementation on metabolic status in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease
- PMID: 29946368
- PMCID: PMC6008939
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-018-0353-2
The effects of probiotic supplementation on metabolic status in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease
Abstract
Background: This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of probiotic supplementation on metabolic profiles in diabetic patients with coronary heart disease (CHD).
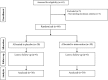
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed among 60 diabetic patients with CHD, aged 40-85 years at a cardiology clinic in Kashan, Iran, from October 2017 through January 2018. Patients were randomly divided into two groups to take either probiotic supplements (n = 30) or placebo (n = 30) for 12 weeks. Fasting blood samples were taken at the beginning of the study and after the 12-week intervention to determine related markers.
Results: After 12-week intervention, probiotic supplementation significantly decreased fasting plasma glucose (β - 20.02 mg/dL; 95% CI - 33.86, - 6.17; P = 0.005), insulin (β - 2.09 µIU/mL; 95% CI - 3.77, - 0.41; P = 0.01), insulin resistance (β - 0.50; 95% CI - 0.96, - 0.03; P = 0.03) and total-/HDL-cholesterol ratio (β - 0.27; 95% CI - 0.52, - 0.03; P = 0.02), and significantly increased insulin sensitivity (β 0.008; 95% CI 0.001, 0.01; P = 0.02) and HDL-cholesterol levels (β 2.52 mg/dL; 95% CI 0.04, 5.00; P = 0.04) compared with the placebo. Moreover, probiotic supplementation led to a significant reduction in serum high sensitivity C-reactive protein (β - 0.88 mg/L; 95% CI - 1.39, - 0.38; P = 0.001), and a significant elevation in total antioxidant capacity (β 108.44 mmol/L; 95% CI 47.61, 169.27; P = 0.001) and total glutathione levels (β 45.15 µmol/L; 95% CI 5.82, 84.47; P = 0.02) compared with the placebo. Probiotic supplementation did not affect other metabolic profiles.
Conclusions: Overall, we found that probiotic supplementation for 12 weeks had beneficial effects on glycemic control, HDL-cholesterol, total-/HDL-cholesterol ratio, biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic patients with CHD.Trial registration Clinical trial registration number http://www.irct.ir: IRCT2017082733941N5.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; Metabolic status; Probiotic; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Similar articles
-
The effects of vitamin D and probiotic co-supplementation on mental health parameters and metabolic status in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Jun 8;84(Pt A):50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29432877 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of probiotic and selenium co-supplementation on mental health parameters and metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Clin Nutr. 2019 Aug;38(4):1594-1598. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Clin Nutr. 2019. Retraction in: Clin Nutr. 2025 Aug 19:S0261-5614(25)00229-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2025.08.015. PMID: 30057015 Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Selenium Supplementation on Metabolic Status in Patients Undergoing for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Surgery: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Oct;191(2):331-337. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-1636-7. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 30637662 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of combined magnesium and zinc supplementation on metabolic status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 May 28;19(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01298-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32466773 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Influences of Chromium Supplementation on Metabolic Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Heart Disease.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Apr;194(2):313-320. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01783-7. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 31243685 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The Promising Role of Microbiome Therapy on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic and Narrative Review.Front Nutr. 2022 May 25;9:906243. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.906243. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35711547 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Inflammatory Markers and Glucose Homeostasis in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 10;12:770861. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.770861. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34955840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced abundance of Fusobacterium signifies cardiovascular benefits of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor in type 2 diabetes: a single arm clinical trial.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 8;16:1600464. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1600464. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40406484 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 Adjuvant Treatment Confers Added Benefits to Patients with Coronary Artery Disease via Target Modulation of the Gut-Heart/-Brain Axes.mSystems. 2022 Apr 26;7(2):e0010022. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00100-22. Epub 2022 Mar 28. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35343796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of probiotics on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in patients with diabetes: a meta-research of meta-analysis studies.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 7;12:1552358. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1552358. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40123937 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials