Cardiovascular disease and brain health: Focus on white matter hyperintensities
- PMID: 29946567
- PMCID: PMC6016077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2018.04.006
Cardiovascular disease and brain health: Focus on white matter hyperintensities
Abstract
Diseases affecting the brain contribute to a substantial proportion of morbidity and mortality in the general population. Conditions such as stroke, dementia and cognitive impairment have a prominent impact on global public health. Despite the heterogeneous clinical manifestations of these conditions and their diverse prognostic implications, current evidence supports a role for cardiovascular disease as a common pathophysiological ground. Brain white matter hyperintensities (WMH) are patchy white matter signal hyperintensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging sequences commonly found in elderly individuals. WMH appear to have a vascular pathogenesis and have been shown to confer an increased risk of stroke and cognitive decline. Indeed, they were proposed as a marker for central nervous system frailty. Cardiovascular diseases seem to play a key role in the etiology of WMH. Carotid atherosclerosis and atrial fibrillation were shown to be associated with higher WMH burden, while adequate blood pressure control has been reported reducing WMH progression. Aim of the present work is to review the available evidence linking WMH to cardiovascular disease, highlighting the complex interplay between cerebral and cardiovascular health.
Figures
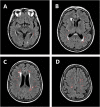
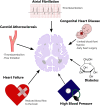
References
-
- Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016Lancet (London, England) 2017;390(10100):1260–1344. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gardener H., Wright C.B., Rundek T., Sacco R.L. Brain health and shared risk factors for dementia and stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015;11(11):651–657. - PubMed
-
- Ylikoski A., Erkinjuntti T., Raininko R., Sarna S., Sulkava R., Tilvis R. White matter hyperintensities on MRI in the neurologically nondiseased elderly. Analysis of cohorts of consecutive subjects aged 55 to 85 years living at home. Stroke. 1995;26(7):1171–1177. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

