Validation and reliability of the rapid diagnostic test 'SD Bioeasy Dengue Duo' for dengue diagnosis in Brazil: a phase III study
- PMID: 29947711
- PMCID: PMC6014722
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760170433
Validation and reliability of the rapid diagnostic test 'SD Bioeasy Dengue Duo' for dengue diagnosis in Brazil: a phase III study
Abstract
Background: The diagnosis of dengue is complex. Until recently, only specialised laboratories were able to confirm dengue infection. However, this has changed with the newly available immunochromatographic rapid tests. Early diagnosis is of great interest, and point-of-care rapid tests have been increasingly used in Brazil. Most of those tests have not undergone validation in the Brazilian population. In this context, we decided to evaluate a rapid test introduced in the Federal District (FD).
Objectives: To estimate the accuracy and reliability of the SD Bioeasy Dengue Duo rapid test and its components to detect dengue infections in a consecutive sample of symptomatic residents in the FD, Brazil.
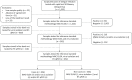
Methods: In total, 1353 venous blood samples were collected between 2013 and 2014. Two hundred and six positive samples (cases) and 246 negative samples (non cases) were required for sensitivity and specificity estimation, respectively; for agreement evaluation, we used 401 samples. The reference standard used was a composite of MAC-ELISA, virus isolation and real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The evaluation was conducted prospectively under field conditions in the public health units of the FD.
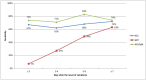
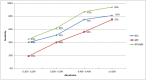
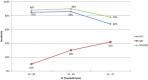
Findings: The results for the overall accuracy of the rapid test (NS1/IgM combined) showed 76% sensitivity and 98% specificity. The sensitivity for the NS1 component (67%) was better than that for the IgM component (35%). The positive likelihood ratio was 46, and the negative likelihood ratio was 0.24. The reliability of the test (NS1/IgM combined) demonstrated crude agreement of 98% (Kappa index 0.94).
Main conclusions: The present phase III, large-scale validation study demonstrates that the rapid test SD Bioeasy Dengue Duo has moderate sensitivity (NS1/IgM combined) and high specificity. Therefore, the test is useful in confirming the diagnosis of dengue, but not enough to rule out the diagnosis. Our results also suggest that Dengue virus (DENV) viral load estimated through the RT-qPCR and antibody level measured through the MAC-ELISA could have had a direct influence on the accuracy of the rapid test.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of diagnostic and analytic performance of the SD Bioline Dengue Duo test for dengue virus (DENV) infections in an endemic area (Savannakhet province, Lao People's Democratic Republic).PLoS One. 2020 Mar 17;15(3):e0230337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230337. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32182271 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Dengue Diagnostic Tests in a Single-Specimen Diagnostic Algorithm.J Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 15;214(6):836-44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw103. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26984143
-
Evaluation of laboratory tests for dengue diagnosis in clinical specimens from consecutive patients with suspected dengue in Belo Horizonte, Brazil.J Clin Virol. 2013 Sep;58(1):41-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jul 17. J Clin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23871166
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis: assessing the accuracy of rapid immunochromatographic tests in dengue diagnosis.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Jun;109(2):116227. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116227. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38503028
-
Rapid immunochromatographic tests for the diagnosis of dengue: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cad Saude Publica. 2020 Jun 8;36(6):e00225618. doi: 10.1590/0102-311X00225618. eCollection 2020. Cad Saude Publica. 2020. PMID: 32520127
Cited by
-
Accuracy of the SD BIOLINE Dengue Duo for rapid point-of-care diagnosis of dengue.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 6;14(3):e0213301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213301. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30840708 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of diagnostic and analytic performance of the SD Bioline Dengue Duo test for dengue virus (DENV) infections in an endemic area (Savannakhet province, Lao People's Democratic Republic).PLoS One. 2020 Mar 17;15(3):e0230337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230337. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32182271 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of novel rapid detection kits for dengue virus NS1 antigen in Dhaka, Bangladesh, in 2017.Virol J. 2019 Aug 15;16(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1204-y. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31416485 Free PMC article.
-
Potential neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects provided by omega-3 (DHA) against Zika virus infection in human SH-SY5Y cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):20119. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56556-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882804 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Dengue Virus Serotype-Specific Non-Structural Protein 1 Capture Immunochromatography Method.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;21(23):7809. doi: 10.3390/s21237809. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34883813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blacksell SD, Jarman RG, Bailey MS, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, Jenjaroen K, Gibbons RV, et al. Evaluation of six commercial point-of-care tests for diagnosis of acute dengue infections: the need for combining NS1 antigen and IgM/IgG antibody detection to achieve acceptable levels of accuracy. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011;18(12):2095–2101. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

