Use of adductor pollicis muscle thickness in hospitalized or ambulatory patients: a systematic review
- PMID: 29947718
- PMCID: PMC6047893
- DOI: 10.1590/1518-8345.2045.2960
Use of adductor pollicis muscle thickness in hospitalized or ambulatory patients: a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: to analyze the use of the Adductor Pollicis Muscle Thickness (APMT) as an anthropometric parameter and prognostic indicator in hospitalized or ambulatory patients.
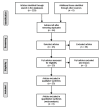
Method: systematic review carried out the Web of Science, SCOPUS and Lilacs databases.
Results: Twenty-three studies were performed on critical, surgical, oncological, nephropathic and hepatopathic patients, collecting data on bibliographic reference, study site, objectives, number of patients, age group, methodology, main results and conclusion. APMT proved to be a good anthropometric parameter for evaluation of nutritional status in critical patients without edema, and surgical, oncological and nephropathic patients, but presented poor performance for diagnosis of malnutrition in hepatopathic patients. It was a good prognostic indicator for mortality in critical, nephropathic and oncological patients, and also a good predictor of hospitalization in nephropathic patients. There was an association with neurological complications in Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) in the case of hepatophatic patients, but it was not a predictor of postoperative complications in surgical patients.
Conclusion: APTM was considered a good anthropometric parameter in most clinical conditions, except in patients with liver disease and a good prognostic indicator for mortality in critical, oncological and nephropathic patients, and a predictor of neurological complications in HE. Further prognostic investigation, standardization of cutoff points and evaluation of sensitivity and specificity are required.
Figures




References
-
- Lameu EB, Gerude MF, Corrêa RC, Lima KA. Adductor pollicis muscle: a new anthropometric parameter. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo. 2004;59(2):57–62. doi: 10.1590/S0041-87812004000200002. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0041-87812004000... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shu-Fen CL, Ong V, Kowitlawakul Y, Ling TA, Mukhopadhyay A, Henry J. The adductor pollicis muscle: a poor predictor of clinical outcome in ICU patients. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2015;24(4):605–609. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.2015.24.4.22. http://apjcn.nhri.org.tw/server/APJCN/24/4/605.pdf - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karst FP, Vieira RM, Barbiero S. Relação da espessura do músculo adutor do polegar e avaliação subjetiva global em unidade de terapia intensiva cardiológica. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2015;27(4):369–375. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20150062. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0103-507X2015000... - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caporossi FS, Caporossi C, Borges Dock-Nascimento D, Aguilar-Nascimento JE. Measurement of the thickness of the adductor pollicis muscle as a predictor of outcomes in critically ill patients. Nutr Hosp. 2012;27(2):490–495. doi: 10.3305/nh.2012.27.2.5514. http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&nrm=iso&lng=pt&tln... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ghorabi S, Ardehali H, Amiri Z, Shariatpanahi ZV. Association of the Adductor Pollicis Muscle Thickness with Clinical Outcomes in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016;31(4):523–526. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26869610 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

