Protective effects of compatible solute ectoine against ethanol-induced toxic alterations in Daphnia magna
- PMID: 29948158
- PMCID: PMC6132719
- DOI: 10.1007/s00360-018-1165-2
Protective effects of compatible solute ectoine against ethanol-induced toxic alterations in Daphnia magna
Abstract
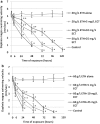
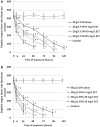
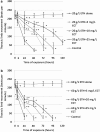
Ectoine (ECT) is a compatible solute synthesized mostly by halophilic microorganisms subjected to various stressful factors. Its protective properties in bacteria and some populations of isolated cells subjected to different stressors are reported; however, little is known on its effects against a commonly used compound, ethanol (ETH). The purpose of our study was to determine the effects of ETH alone (at 20 and 60 g/L) and in the combination with various concentrations of ECT (5, 10, and 25 mg/L) at various times of exposure on behavioural, physiological, and biochemical parameters of a model invertebrate Daphnia magna. In the present study, we determined the following parameters: immobilisation, heart rate, thoracic limb movement, catalase (CAT) activity, and nitric oxide species (NOx) level. Our study revealed that both concentrations of ETH alone induced immobilisation and decrease of swimming velocity, heart rate, and thoracic limb activity; however, catalase activity and NOx levels were increased. On the other hand, the animals exposed to the combinations of ETH + ECT showed a reduced immobilisation and alleviated inhibition of heart rate and thoracic limb activity, lower increase of CAT activity, and NOx level when compared to the crustaceans subjected to ETH alone. The most distinct alleviation of toxic effects was noted in the combinations in which the highest concentration of ECT were used. The results suggest that ETH may induce oxidative stress in daphnids and attenuating effects of ECT probably result from its antioxidative properties.
Keywords: Daphnia magna; Ectoine; Ethanol; Protective effects.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ectoine alleviates behavioural, physiological and biochemical changes in Daphnia magna subjected to formaldehyde.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Oct;22(20):15549-62. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4747-5. Epub 2015 May 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26006078
-
Protective effects of ectoine on behavioral, physiological and biochemical parameters of Daphnia magna subjected to hydrogen peroxide.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;170:38-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25704915
-
Protective effects of ectoine on heat-stressed Daphnia magna.J Comp Physiol B. 2014 Dec;184(8):961-76. doi: 10.1007/s00360-014-0860-x. Epub 2014 Sep 16. J Comp Physiol B. 2014. PMID: 25223383 Free PMC article.
-
Daphnia magna model in the toxicity assessment of pharmaceuticals: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Apr 1;763:143038. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143038. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33127157 Review.
-
Ectoine as a promising protective agent in humans and animals.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2016 Dec 1;67(4):260-265. doi: 10.1515/aiht-2016-67-2837. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2016. PMID: 28033102 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods to Induce Analgesia and Anesthesia in Crustaceans: A Supportive Decision Tool.Biology (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;12(3):387. doi: 10.3390/biology12030387. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979080 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Aziz H, Wadi W, Abdallah DM, Lentzen G, Khayyal MT. Novel effects of ectoine, a bacteria-derived natural tetrahydropyrimidine, in experimental colitis. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol. 2013;20:585–591. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Testing and Materials . Standard practice for conducting static acute toxicity tests on wastewaters with Daphnia: annual book of ASTM standards. Philadelphia: ASTM; 1986. pp. D4229–D4284.
-
- Barros S (2013) Brazil biofuels annual. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. Gain Report (BR13005)
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

