Central serotonin modulates neural responses to virtual violent actions in emotion regulation networks
- PMID: 29948188
- PMCID: PMC6698268
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-018-1693-2
Central serotonin modulates neural responses to virtual violent actions in emotion regulation networks
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Central serotonin modulates neural responses to virtual violent actions in emotion regulation networks.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Dec;224(9):3409. doi: 10.1007/s00429-019-01927-4. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 31392402 Free PMC article.
Abstract
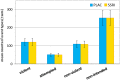
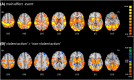
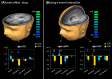
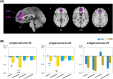
Disruptions in the cortico-limbic emotion regulation networks have been linked to depression, anxiety, impulsivity, and aggression. Altered transmission of the central nervous serotonin (5-HT) contributes to dysfunctions in the cognitive control of emotions. To date, studies relating to pharmaco-fMRI challenging of the 5-HT system have focused on emotion processing for facial expressions. We investigated effects of a single-dose selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitor (escitalopram) on emotion regulation during virtual violence. For this purpose, 38 male participants played a violent video game during fMRI scanning. The SSRI reduced neural responses to violent actions in right-hemispheric inferior frontal gyrus and medial prefrontal cortex encompassing the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), but not to non-violent actions. Within the ACC, the drug effect differentiated areas with high inhibitory 5-HT1A receptor density (subgenual s25) from those with a lower density (pregenual p32, p24). This finding links functional responses during virtual violent actions with 5-HT neurotransmission in emotion regulation networks, underpinning the ecological validity of the 5-HT model in aggressive behavior. Available 5-HT receptor density data suggest that this SSRI effect is only observable when inhibitory and excitatory 5-HT receptors are balanced. The observed early functional changes may impact patient groups receiving SSRI treatment.
Keywords: Medial prefrontal cortex; Pharmaco-fMRI; SSRI; Serotonin; Virtual violence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of 5-HT in response inhibition and re-engagement.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Aug;23(8):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23816061 Clinical Trial.
-
Amygdala activity after subchronic escitalopram administration in healthy volunteers: A pharmaco-functional magnetic resonance imaging study.J Psychopharmacol. 2024 Dec;38(12):1071-1082. doi: 10.1177/02698811241286773. Epub 2024 Oct 4. J Psychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39364684 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of 5-HTTLPR on SSRI serotonin transporter blockade during emotion regulation: A preliminary fMRI study.J Affect Disord. 2016 May 15;196:11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.02.019. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Affect Disord. 2016. PMID: 26896742 Clinical Trial.
-
Serotonergic Regulation of Prefrontal Cortical Circuitries Involved in Cognitive Processing: A Review of Individual 5-HT Receptor Mechanisms and Concerted Effects of 5-HT Receptors Exemplified by the Multimodal Antidepressant Vortioxetine.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):970-86. doi: 10.1021/cn500340j. Epub 2015 Mar 16. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25746856 Review.
-
[Escitalopram: a selective inhibitor and allosteric modulator of the serotonin transporter].Encephale. 2007 Dec;33(6):965-72. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2007.11.001. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Encephale. 2007. PMID: 18789789 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Behavioral, cortical and autonomic effects of single-dose escitalopram on the induction and regulation of fear and disgust: Comparison with single-session psychological emotion regulation with reappraisal.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jan 4;13:988893. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.988893. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36684004 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretation of Social Interactions: Functional Imaging of Cognitive-Semiotic Categories During Naturalistic Viewing.Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 Aug 14;12:296. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00296. eCollection 2018. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30154703 Free PMC article.
-
REVERSE phenotyping-Can the phenotype following constitutive Tph2 gene inactivation in mice be transferred to children and adolescents with and without adhd?Brain Behav. 2021 May;11(5):e02054. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2054. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33523602 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral intervention with task repetition compared to pharmacological intervention with SSRI for enhancement of cognitive control in emotional and non-emotional settings.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06835-6. Online ahead of print. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40536716
-
The Implication of 5-HT Receptor Family Members in Aggression, Depression and Suicide: Similarity and Difference.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 8;23(15):8814. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158814. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adachi PJC, Willoughby T. The effect of video game competition and violence on aggressive behavior: which characteristic has the greatest influence? Psychol Violence. 2011;1:259–274. doi: 10.1037/a0024908. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

