Predictors of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease in children: a meta-analysis of 4442 cases
- PMID: 29948255
- PMCID: PMC6061038
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-018-3182-2
Predictors of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease in children: a meta-analysis of 4442 cases
Abstract
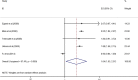
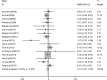
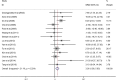
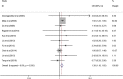
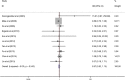
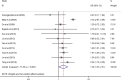
The purpose of this study was to identify the clinical features and laboratory factors that are predictive of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)-resistant Kawasaki disease. Multiple databases were searched for relevant studies on IVIG-resistant Kawasaki disease published from January 2002 to April 2017. Eligible studies were retrieved by manual review of the references. Stata 12 was used for the meta-analysis. Weighted mean differences and odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated for several indices. Twenty-eight studies involving 26,260 patients comprising 4442 IVIG-resistant Kawasaki disease patients and 21,818 IVIG-sensitive Kawasaki disease patients were included. The meta-analysis showed that the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in the IVIG-resistant group was significantly higher than that in the IVIG-sensitive group, and that platelet count and hemoglobin levels were significantly lower in the IVIG-resistant group. The patients with oral mucosa alterations, cervical lymphadenopathy, swelling of the extremities, polymorphous rash, and initial administration of IVIG ≤ 4.0 days after the onset of symptoms were more likely to be IVIG resistant.
Conclusion: The initial administration of IVIG ≤ 4.0 days after the onset of symptoms increased ESR and decreased hemoglobin and platelet counts, oral mucosa alterations, cervical lymphadenopathy, swelling of the extremities, and polymorphous rash and are the risk factors for IVIG-resistant Kawasaki disease. What is Known: • Recent reports on this topic are about aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gammaglutamyl transferase, total bilirubin, white blood cells, platelets, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN), C-reactive protein (CRP), pro-brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), albumin, and sodium as the risk factors in the IVIG-resistant Kawasaki disease; however, no studies have been published on clinical features as predictors of IVIG resistance. What is New: • This meta-analysis identified the clinical features, the initial administration of IVIG ≤ 4.0 days after the onset of symptoms, and much more comprehensive laboratory indicators, such as hemoglobin, as predictors of IVIG-resistant Kawasaki disease.
Keywords: Intravenous immunoglobulin; Kawasaki disease; Meta-analysis; Risk.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
None.
Figures



References
-
- Campbell AJ, Burns JC. Adjunctive therapies for Kawasaki disease. J Inf Secur. 2016;72(Suppl):S1–S5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81370217/the Chinese Natural Science Foundation
- 8157021282/the Chinese Natural Science Foundation
- 31600695/the National Natural Science Foundation for Youth
- 81600391/the National Natural Science Foundation for Youth
- 16KJB310014/the Universities Natural Science Foundation of Jingasu Province
- SYS201642/the Applied Foundational Research of Medical and Health Care of Suzhou City
- BK20150291/Jiangsu Provincial Science Foundation of Young
- QNRC 2016756/Jiangsu Provincial Medical Young Talents
- SYS201557/the Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau
- SYS201443/the Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau
- SYS201633/the Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau
- KJXW2014015/the Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

