Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2011
- PMID: 29948477
- PMCID: PMC6021481
- DOI: 10.1007/s10388-018-0614-z
Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2011
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Comprehensive Registry of Esophageal Cancer in Japan, 2011.Esophagus. 2018 Oct;15(4):304-305. doi: 10.1007/s10388-018-0624-x. Esophagus. 2018. PMID: 29948478 Free PMC article.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethical Statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
All authors have nothing to disclose with regard to commercial support.
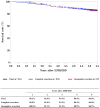
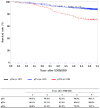
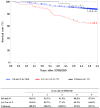
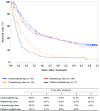
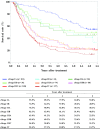
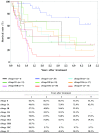
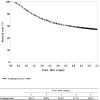
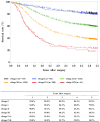
Figures
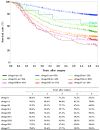
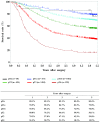
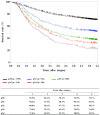
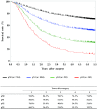
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
