Interdependence between iron acquisition and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 29948830
- PMCID: PMC6221862
- DOI: 10.1007/s12275-018-8114-3
Interdependence between iron acquisition and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
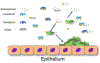
Bacterial biofilms remain a persistent threat to human healthcare due to their role in the development of antimicrobial resistance. To combat multi-drug resistant pathogens, it is crucial to enhance our understanding of not only the regulation of biofilm formation, but also its contribution to bacterial virulence. Iron acquisition lies at the crux of these two subjects. In this review, we discuss the role of iron acquisition in biofilm formation and how hosts impede this mechanism to defend against pathogens. We also discuss recent findings that suggest that biofilm formation can also have the reciprocal effect, influencing siderophore production and iron sequestration.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; biofilm; exopolysaccharides; iron acquisition; nutritional immunity; siderophore.
Figures

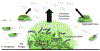
References
-
- Alhede M, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M, and Alhede M 2014. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: mechanisms of immune evasion. Adv. Appl. Microbiol 86, 1–40. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GG and O’Toole GA 2008. Innate and induced resistance mechanisms of bacterial biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol 322, 85–105. - PubMed
-
- Ardehali R, Shi L, Janatova J, Mohammad SF, and Burns GL 2002. The effect of apo-transferrin on bacterial adhesion to bio-materials. Artif. Organs 26, 512–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

