Mesoporous Silicon Particles Favor the Induction of Long-Lived Humoral Responses in Mice to a Peptide-Based Vaccine
- PMID: 29949862
- PMCID: PMC6073586
- DOI: 10.3390/ma11071083
Mesoporous Silicon Particles Favor the Induction of Long-Lived Humoral Responses in Mice to a Peptide-Based Vaccine
Abstract
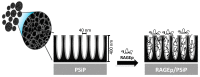
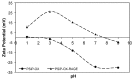
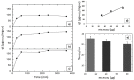
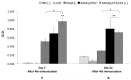
Vaccinology faces the challenge of developing improved immunization approaches that are able to induce long-term immunity with the desired Th profile according to the pathology. In this context, new vehicles for efficient antigen delivery that exert adjuvant effects play a critical role in addressing this goal. Herein, mesoporous silicon particles (PSiP) were assessed as carriers for a peptide-based vaccine targeting the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), which is a relevant receptor in Alzheimer´s disease and other diseases. A RAGE peptide was adsorbed onto PSiP (PSiP vaccine) and administered to BALB/c mice, leading to immune responses that were similar in magnitude to those induced by the soluble peptide. However, the response induced by PSiP lasted for a significantly longer period when compared with the behavior of the group immunized with the peptide alone. Therefore, PSiP are proposed as carriers to enhance immune memory, which is critical in vaccination. This study opens interesting perspectives related to the application of PSiP in vaccinology.
Keywords: adjuvant; humoral response; peptide vaccine; receptor for advanced glycation end products; vaccine delivery vehicle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this work declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Navarro-Tovar G., Wong-Arce A., Campos-Portillo M., Palestino G., Rosales-Mendoza S. The Potential of Porous Silicon Particles for Multi-Epitopic Vaccine Development. Mesoporous Biomater. 2016;3:83–92. doi: 10.1515/mesbi-2016-0012. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

