Synthesis and Comparative Evaluation of Novel Cationic Amphiphile C12-Man-Q as an Efficient DNA Delivery Agent In Vitro
- PMID: 29949910
- PMCID: PMC6100083
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071540
Synthesis and Comparative Evaluation of Novel Cationic Amphiphile C12-Man-Q as an Efficient DNA Delivery Agent In Vitro
Abstract
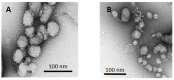
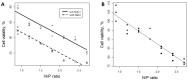
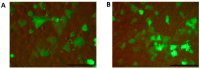
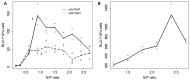
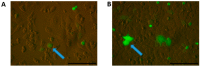
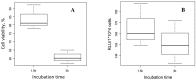
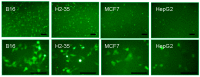
New amphiphilic 1,4-DHP derivative C12-Man-Q with remoted cationic moieties at positions 2 and 6 was synthesised to study DNA delivery activity. The results were compared with data obtained for cationic 1,4-DHP derivative D19, which is known to be the most efficient one among the previously tested 1,4-DHP amphiphiles. We analysed the effects of C12-Man-Q concentration, complexation media, and complex/cell contact time on the gene delivery effectiveness and cell viability. Transmission electron microscopy data confirms that lipoplexes formed by the compound C12-Man-Q were quite uniform, vesicular-like structures with sizes of about 50 nm, and lipoplexes produced by compound D19 were of irregular shapes, varied in size in the range of 25⁻80 nm. Additionally, confocal microscopy results revealed that both amphiphiles effectively delivered green fluorescent protein expression plasmid into BHK-21 cells and produced a fluorescent signal with satisfactory efficiency, although compound C12-Man-Q was more cytotoxic to the BHK-21 cells with an increase of concentration. It can be concluded that optimal conditions for C12-Man-Q lipoplexes delivery in BHK-21 cells were the serum free media without 0.15 M NaCl, at an N/P ratio of 0.9. Compound D19 showed higher transfection efficiency to transfect BHK-21 and Cos-7 cell lines, when transfecting active proliferating cells. Although D19 was not able to transfect all studied cell lines we propose that it could be cell type specific. The compound C12-Man-Q showed modest delivery activity in all used cell lines, and higher activity was obtained in the case of H2-35 and B16 cells. The transfection efficiency in cell lines MCF-7, HeLa, and Huh-7 appears to be comparable to the reference compound D19 and minimal in the HepG2 cell line.
Keywords: 1,4-dihydropyridines; DNA transfection; cationic amphiphiles; cytotoxicity; gene delivery; lipoplexes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Novel cationic amphiphilic 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives for DNA delivery.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Dec 20;1509(1-2):451-66. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00327-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11118554
-
The influence of the structural orientation of amide linkers on the serum compatibility and lung transfection properties of cationic amphiphiles.Biomaterials. 2011 Aug;32(22):5231-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.03.059. Epub 2011 Apr 17. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21501864
-
Dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine and PEG-lipid conjugates modify DNA delivery mediated by 1,4-dihydropyridine amphiphiles.J Control Release. 2004 Sep 14;99(1):177-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.06.019. J Control Release. 2004. PMID: 15342190
-
Arginine-based cationic liposomes for efficient in vitro plasmid DNA delivery with low cytotoxicity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1361-75. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S38903. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23630419 Free PMC article.
-
How does the spacer length of cationic gemini lipids influence the lipoplex formation with plasmid DNA? Physicochemical and biochemical characterizations and their relevance in gene therapy.Biomacromolecules. 2012 Dec 10;13(12):3926-37. doi: 10.1021/bm301066w. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Biomacromolecules. 2012. PMID: 23130552
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic Properties of Amphiphilic Dihydropyridines, Dihydropyridones, and Aminovinylcarbonyl Compounds.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Dec 31;2020:8413713. doi: 10.1155/2020/8413713. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33488932 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoplexes' Structure, Preparation, and Role in Managing Different Diseases.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Jun 7;25(5):131. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02850-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38849687 Review.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Amphiphilic N-Benzyl 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivatives-Evaluation of Lipid Monolayer and Self-Assembling Properties.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;16(12):4206. doi: 10.3390/ma16124206. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374390 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Self-Assembling bis-1,4-Dihydropyridines: Detailed Studies of Bromination of Four Methyl Groups and Bromine Nucleophilic Substitution.Molecules. 2023 Dec 27;29(1):161. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010161. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202746 Free PMC article.
-
Data for characterisation of nanoformulations formed by cationic 1,4-dihydopyridine and calix[4]arene compositions.Data Brief. 2022 Feb 23;41:107988. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.107988. eCollection 2022 Apr. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35252501 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

