Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaves Extract on High Glucose-Induced Metabolic Changes in HepG2 Cells
- PMID: 29949946
- PMCID: PMC6164683
- DOI: 10.3390/biology7030037
Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaves Extract on High Glucose-Induced Metabolic Changes in HepG2 Cells
Abstract
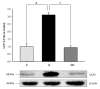
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of diabetes, but the metabolic alterations during early stages of the disease remain unknown. The ability of liver cells to rearrange their metabolism plays an important role in compensating the energy shortage and may provide cell survival. Moringa oleifera leaves have been studied for its health properties against diabetes, insulin resistance, and non-alcoholic liver disease. We postulated that M. oleifera executes a protective function on mitochondrial functionality in HepG2 treated with high glucose. We evaluated the effect of high glucose treatment on the mitochondrial function of HepG2 cells using a Seahorse extracellular flux analyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE), and western blot analysis. For assessment of mitochondrial abnormalities, we measured the activity of mitochondrial Complex I and IV as well as uncoupling protein 2, and sirtuin 3 protein contents. Our results demonstrate that, under conditions mimicking the hyperglycemia, Complex I activity, UCP2, Complex III and IV subunits content, supercomplex formation, and acetylation levels are modified with respect to the control condition. However, basal oxygen consumption rate was not affected and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production remained unchanged in all groups. Treatment of HepG2 cells with M. oleifera extract significantly increased both protein content and mitochondrial complexes activities. Nonetheless, control cells’ respiratory control ratio (RCR) was 4.37 compared to high glucose treated cells’ RCR of 15.3, and glucose plus M. oleifera treated cells’ RCR of 5.2, this indicates high-quality mitochondria and efficient oxidative phosphorylation coupling. Additionally, the state app was not altered between different treatments, suggesting no alteration in respiratory fluxes. These findings enhance understanding of the actions of M. oleifera and suggest that the known antidiabetic property of this plant, at least in part, is mediated through modulating the mitochondrial respiratory chain.
Keywords: HepG2 cells; Moringa oleifera; SIRT3; UCP2; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Aa A.B., Om J., Ts E., Ga A. Preliminary phytochemical screening, antioxidant and antihyperglycaemic activity of Moringa oleifera leaf extracts. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017;30:2217–2222. - PubMed
-
- Makkar H.P.S., Becker K. Nutrional value and antinutritional components of whole and ethanol extracted Moringa oleifera leaves. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996;63:211–228. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(96)01023-1. - DOI
-
- Tabbon P., Sripanidkulchai B., Sripanidkulchai K. Hypocholesterolemic mechanism of phenolics-enriched extract from Moringa oleifera leaves in HepG2 cell lines. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2016;38:155–161.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

