Viral quasispecies reconstruction via tensor factorization with successive read removal
- PMID: 29949976
- PMCID: PMC6022648
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty291
Viral quasispecies reconstruction via tensor factorization with successive read removal
Abstract
Motivation: As RNA viruses mutate and adapt to environmental changes, often developing resistance to anti-viral vaccines and drugs, they form an ensemble of viral strains--a viral quasispecies. While high-throughput sequencing (HTS) has enabled in-depth studies of viral quasispecies, sequencing errors and limited read lengths render the problem of reconstructing the strains and estimating their spectrum challenging. Inference of viral quasispecies is difficult due to generally non-uniform frequencies of the strains, and is further exacerbated when the genetic distances between the strains are small.
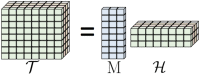
Results: This paper presents TenSQR, an algorithm that utilizes tensor factorization framework to analyze HTS data and reconstruct viral quasispecies characterized by highly uneven frequencies of its components. Fundamentally, TenSQR performs clustering with successive data removal to infer strains in a quasispecies in order from the most to the least abundant one; every time a strain is inferred, sequencing reads generated from that strain are removed from the dataset. The proposed successive strain reconstruction and data removal enables discovery of rare strains in a population and facilitates detection of deletions in such strains. Results on simulated datasets demonstrate that TenSQR can reconstruct full-length strains having widely different abundances, generally outperforming state-of-the-art methods at diversities 1-10% and detecting long deletions even in rare strains. A study on a real HIV-1 dataset demonstrates that TenSQR outperforms competing methods in experimental settings as well. Finally, we apply TenSQR to analyze a Zika virus sample and reconstruct the full-length strains it contains.
Availability and implementation: TenSQR is available at https://github.com/SoYeonA/TenSQR.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
Similar articles
-
aBayesQR: A Bayesian Method for Reconstruction of Viral Populations Characterized by Low Diversity.J Comput Biol. 2018 Jul;25(7):637-648. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2017.0249. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29480740
-
QSdpR: Viral quasispecies reconstruction via correlation clustering.Genomics. 2018 Nov;110(6):375-381. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29268961
-
De novo haplotype reconstruction in viral quasispecies using paired-end read guided path finding.Bioinformatics. 2018 Sep 1;34(17):2927-2935. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty202. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29617936
-
Benchmarking of viral haplotype reconstruction programmes: an overview of the capacities and limitations of currently available programmes.Brief Bioinform. 2014 May;15(3):431-42. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs081. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Brief Bioinform. 2014. PMID: 23257116 Review.
-
Application of deep sequencing methods for inferring viral population diversity.J Virol Methods. 2019 Apr;266:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30690049 Review.
Cited by
-
VirStrain: a strain identification tool for RNA viruses.Genome Biol. 2022 Jan 31;23(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02609-x. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35101081 Free PMC article.
-
Incipient functional SARS-CoV-2 diversification identified through neural network haplotype maps.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Mar 5;121(10):e2317851121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2317851121. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38416684 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mutant Spectra at Different Depth Levels Reveal an Overwhelming Abundance of Low Frequency Mutations.Pathogens. 2022 Jun 8;11(6):662. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11060662. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35745516 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of haplotype callers for next-generation sequencing of viruses.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Aug;82:104277. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104277. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32151775 Free PMC article.
-
Quasispecies Fitness Partition to Characterize the Molecular Status of a Viral Population. Negative Effect of Early Ribavirin Discontinuation in a Chronically Infected HEV Patient.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 24;23(23):14654. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314654. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn S., Vikalo H. (2017) aBayesQR: a Bayesian method for reconstruction of viral populations characterized by low diversity In: International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology. Springer, Hong Kong, pp. 353–369. - PubMed
-
- Cai C. et al. (2016) Structured low-rank matrix factorization for haplotype assembly. IEEE J. Selected Topics Signal Process., 10, 647–657.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

