Matrix abnormalities in pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 29950306
- PMCID: PMC9489108
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0033-2018
Matrix abnormalities in pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
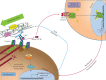
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating, progressive disease, marked by excessive scarring, which leads to increased tissue stiffness, loss in lung function and ultimately death. IPF is characterised by progressive fibroblast and myofibroblast proliferation, and extensive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Myofibroblasts play a key role in ECM deposition. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 is a major growth factor involved in myofibroblast differentiation, and the creation of a profibrotic microenvironment. There is a strong link between increased ECM stiffness and profibrotic changes in cell phenotype and differentiation. The activation of TGF-β1 in response to mechanical stress from a stiff ECM explains some of the influence of the tissue microenvironment on cell phenotype and function. Understanding the close relationship between cells and their surrounding microenvironment will ultimately facilitate better management strategies for IPF.
Copyright ©ERS 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Kolb reports a research grant from Intermune/Roche Canada, during the conduct of the study. He also reports grants and personal fees from Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim and GSK, personal fees from Gilead, Prometic and Genoa, and grants from Actelion, Respivert, Alkermes and Pharmaxis, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: C. Upagupta reports grants from the Canadian Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study. Conflict of interest: C. Shimbori reports grants from the Canadian Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study.
Figures
Comment in
References
-
- Selman M, Pardo A. Revealing the pathogenic and aging-related mechanisms of the enigmatic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An integral model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014; 189: 1161–1172. - PubMed
-
- Vancheri C, Failla M, Crimi N, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a disease with similarities and links to cancer biology. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 496–504. - PubMed
-
- Ley B, Collard HR, King TE. Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 183: 431–440. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Selman M. Nintedanib and pirfenidone. New antifibrotic treatments indicated for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis offer hopes and raises questions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015; 191: 252–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
