Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Nonstructural Membrane Protein pK15 Recruits the Class II Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase PI3K-C2α To Activate Productive Viral Replication
- PMID: 29950425
- PMCID: PMC6096797
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00544-18
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Nonstructural Membrane Protein pK15 Recruits the Class II Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase PI3K-C2α To Activate Productive Viral Replication
Abstract
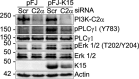
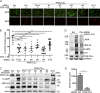
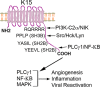
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)/human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) causes the angiogenic tumor KS and two B-cell malignancies. The KSHV nonstructural membrane protein encoded by the open reading frame (ORF) K15 recruits and activates several cellular proteins, including phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1), components of the NF-κB pathway, as well as members of the Src family of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, and thereby plays an important role in the activation of angiogenic and inflammatory pathways that contribute to the pathogenesis of KS as well as KSHV productive (lytic) replication. In order to identify novel cellular components involved in the biology of pK15, we immunoprecipitated pK15 from KSHV-infected endothelial cells and identified associated proteins by label-free quantitative mass spectrometry. Cellular proteins interacting with pK15 point to previously unappreciated cellular processes, such as the endocytic pathway, that could be involved in the function of pK15. We found that the class II phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) PI3K-C2α, which is involved in the endocytosis of activated receptor tyrosine kinases and their signaling from intracellular organelles, interacts and colocalizes with pK15 in vesicular structures abundant in the perinuclear area. Further functional analysis revealed that PI3K-C2α contributes to the pK15-dependent phosphorylation of PLCγ1 and Erk1/2. PI3K-C2α also plays a role in KSHV lytic replication, as evidenced by the reduced expression of the viral lytic genes K-bZIP and ORF45 as well as the reduced release of infectious virus in PI3K-C2α-depleted KSHV-infected endothelial cells. Taken together, our results suggest a role of the cellular PI3K-C2α protein in the functional properties of the KSHV pK15 protein.IMPORTANCE The nonstructural membrane protein encoded by open reading frame K15 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) (HHV8) activates several intracellular signaling pathways that contribute to the angiogenic properties of KSHV in endothelial cells and to its reactivation from latency. A detailed understanding of how pK15 activates these intracellular signaling pathways is a prerequisite for targeting these processes specifically in KSHV-infected cells. By identifying pK15-associated cellular proteins using a combination of immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry, we provide evidence that pK15-dependent signaling may occur from intracellular vesicles and rely on the endocytotic machinery. Specifically, a class II PI3K, PI3K-C2α, is recruited by pK15 and involved in pK15-dependent intracellular signaling and viral reactivation from latency. These findings are of importance for future intervention strategies that aim to disrupt the activation of intracellular signaling by pK15 in order to antagonize KSHV productive replication and tumorigenesis.
Keywords: KSHV-K15; PI3K-C2α; lytic replication.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) non-structural membrane protein K15 is required for viral lytic replication and may represent a therapeutic target.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Sep 22;13(9):e1006639. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006639. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28938025 Free PMC article.
-
ARID3B: a Novel Regulator of the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Cycle.J Virol. 2016 Sep 29;90(20):9543-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03262-15. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27512077 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF21 Tyrosine Kinase and Viral Lytic Reactivation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Approved for Clinical Use.J Virol. 2020 Feb 14;94(5):e01791-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01791-19. Print 2020 Feb 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31826996 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of KSHV Latency and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):1034. doi: 10.3390/v12091034. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32957532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus replication.Semin Cancer Biol. 2009 Jun;19(3):153-7. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2009.02.010. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009. PMID: 19429478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recruitment of phospholipase Cγ1 to the non-structural membrane protein pK15 of Kaposi Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus promotes its Src-dependent phosphorylation.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 18;17(6):e1009635. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009635. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34143834 Free PMC article.
-
Awakening the sleeping giant: Epstein-Barr virus reactivation by biological agents.Pathog Dis. 2024 Feb 7;82:ftae002. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftae002. Pathog Dis. 2024. PMID: 38281067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Class II Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022;436:51-68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06566-8_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36243839
-
Modulation of Lymphotoxin β Surface Expression by Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus K3 Through Glycosylation Interference.J Med Virol. 2025 Jan;97(1):e70179. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70179. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 39831393 Free PMC article.
-
Cancers associated with human gammaherpesviruses.FEBS J. 2022 Dec;289(24):7631-7669. doi: 10.1111/febs.16206. Epub 2021 Oct 2. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34536980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, Babinet P, d'Agay MF, Clauvel JP, Raphael M, Degos L, Sigaux F. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood 86:1276–1280. - PubMed
-
- Dupin N, Fisher C, Kellam P, Ariad S, Tulliez M, Franck N, van Marck E, Salmon D, Gorin I, Escande JP, Weiss RA, Alitalo K, Boshoff C. 1999. Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 latently infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma, multicentric Castleman's disease, and primary effusion lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4546–4551. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

