Structure of a human synaptic GABAA receptor
- PMID: 29950725
- PMCID: PMC6220708
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0255-3
Structure of a human synaptic GABAA receptor
Abstract
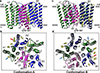
Fast inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain is principally mediated by the neurotransmitter GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) and its synaptic target, the type A GABA receptor (GABAA receptor). Dysfunction of this receptor results in neurological disorders and mental illnesses including epilepsy, anxiety and insomnia. The GABAA receptor is also a prolific target for therapeutic, illicit and recreational drugs, including benzodiazepines, barbiturates, anaesthetics and ethanol. Here we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human α1β2γ2 GABAA receptor, the predominant isoform in the adult brain, in complex with GABA and the benzodiazepine site antagonist flumazenil, the first-line clinical treatment for benzodiazepine overdose. The receptor architecture reveals unique heteromeric interactions for this important class of inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor. This work provides a template for understanding receptor modulation by GABA and benzodiazepines, and will assist rational approaches to therapeutic targeting of this receptor for neurological disorders and mental illness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


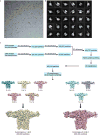
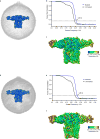

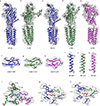

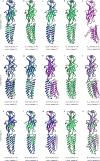
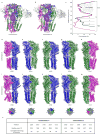
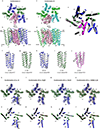
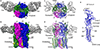

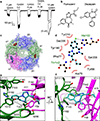

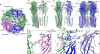
Comment in
-
Key receptor involved in neuronal signalling visualized.Nature. 2018 Jul;559(7712):37-38. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05538-7. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29967383 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

