Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia Repair With Urinary Bladder Matrix Graft
- PMID: 29950797
- PMCID: PMC6002250
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2017.00100
Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia Repair With Urinary Bladder Matrix Graft
Abstract
Background and objectives: Paraesophageal hiatal hernia repair can be performed with or without mesh reinforcement. The use, technique, and mesh type remain controversial because of mixed reports on mesh-related complications. Short-term outcomes have become important in all forms of surgery.
Methods: From January 2012 through April 2017, all patients who underwent isolated hiatal hernia repair in our center were reviewed. Concomitant bariatric surgery cases were excluded. Repairs reinforced by porcine urinary bladder matrix (UBM) graft were compared to non-UBM repairs. Statistical comparison was based on a Wilcoxon 2-sample test or Fisher's exact test.
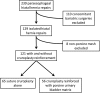
Results: We reviewed 239 charts; 110 bariatric cases and 8 cases with non-UBM reinforcement were excluded. We identified 121 patients: 56 UBM-reinforced (46.3%) versus 65 non-UBM (53.7%). Sixteen (28.6%) UBM cases were male versus 23 (35.4%) non-UBM cases. The UBM patients were significantly older (63.9 versus 54.3; P = .001). There was no difference in mean BMI (29.6 vs 28.5; P = .28). Cases were performed laparoscopically (60.7% vs 67.7%; P = .45) or robotically (39.3% vs 32.3%; P = .45), with no conversions to open. The UBM group had a longer mean operative time (183 minutes vs 139 minutes; P = .001).There was no difference in median length of stay (2 days vs 2 days; P = .09) or 30-day readmission rate (7.1% vs 7.5%; P =.99). Postoperative complications were graded according to the Clavien-Dindo classification, and there was no difference (19.6% vs 9.2%; P = .12).
Conclusions: Hiatal hernia repair with UBM reinforcement can be performed safely with no increase in postoperative complications.
Keywords: Cruroplasty; Fundoplication; Mesh; Paraesophageal hiatal hernia; Urinary bladder matrix.
Similar articles
-
Large Hiatal Hernia Repair with Urinary Bladder Matrix Graft Reinforcement and Concomitant Sleeve Gastrectomy.JSLS. 2019 Jan-Mar;23(1):e2018.00106. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2018.00106. JSLS. 2019. PMID: 30880900 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Bladder Matrix Reinforcement for Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Repair.JSLS. 2018 Apr-Jun;22(2):e2017.00060. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2017.00060. JSLS. 2018. PMID: 29861621 Free PMC article.
-
Hiatal Hernia Repair with Novel Biological Graft Reinforcement.JSLS. 2016 Apr-Jun;20(2):e2016.00016. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2016.00016. JSLS. 2016. PMID: 27186066 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Techniques for Robotically-Assisted Laparoscopic Paraesophageal Hernia Repair.Thorac Surg Clin. 2019 Nov;29(4):369-377. doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Thorac Surg Clin. 2019. PMID: 31564393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of giant paraesophageal hernia: pro laparoscopic approach.Hernia. 2018 Dec;22(6):909-919. doi: 10.1007/s10029-017-1706-8. Epub 2017 Nov 25. Hernia. 2018. PMID: 29177588 Review.
Cited by
-
Large Hiatal Hernia Repair with Urinary Bladder Matrix Graft Reinforcement and Concomitant Sleeve Gastrectomy.JSLS. 2019 Jan-Mar;23(1):e2018.00106. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2018.00106. JSLS. 2019. PMID: 30880900 Free PMC article.
-
Novel "starburst" mesh configuration for paraesophageal and recurrent hiatal hernia repair: comparison with keyhole mesh configuration.Surg Endosc. 2023 Mar;37(3):2239-2246. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09447-9. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 35902405
-
Narrative review of management controversies for paraesophageal hernia.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Jul;13(7):4476-4483. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-720. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34422374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kahrilas PJ, Hirano I. Diseases of the Esophagus. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed McGraw-Hill Medical; Chapter 347, 2014. http://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=1130§ionid=7... Accessed September 28, 2017.
-
- Roman S, Kahrilas PJ. The diagnosis and management of hiatus hernia. BMJ. 2014;349:g6154. - PubMed
-
- Kohn GP, Price RR, DeMeester SR, et al. Guidelines for the management of hiatal hernia. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:4409–4428. - PubMed
-
- Zehetner J, DeMeester SR, Ayazi S, et al. Laparoscopic versus open repair of paraesophageal hernia: the second decade. J Am Coll Surg. 2011;212:813–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous