Linezolid: a review of its properties, function, and use in critical care
- PMID: 29950810
- PMCID: PMC6014438
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S164515
Linezolid: a review of its properties, function, and use in critical care
Abstract
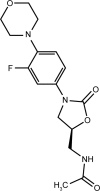
Linezolid can be considered as the first member of the class of oxazolidinone antibiotics. The compound is a synthetic antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis through binding to rRNA. It also inhibits the creation of the initiation complex during protein synthesis which can reduce the length of the developed peptide chains, and decrease the rate of reaction of translation elongation. Linezolid has been approved for the treatment of infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, hospital-acquired pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus, complicated skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), uncomplicated SSSIs caused by methicillin-susceptible S. aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes, and community-acquired pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Analysis of high-resolution structures of linezolid has demonstrated that it binds a deep cleft of the 50S ribosomal subunit that is surrounded by 23S rRNA nucleotides. Mutation of 23S rRNA was shown to be a linezolid resistance mechanism. Besides, mutations in specific regions of ribosomal proteins uL3 and uL4 are increasingly associated with linezolid resistance. However, these proteins are located further away from the bound drug. The methicillin-resistant S. aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci are considered the most common Gram-positive bacteria found in intensive care units (ICUs), and linezolid, as an antimicrobial drug, is commonly utilized to treat infected ICU patients. The drug has favorable in vitro and in vivo activity against the mentioned organisms and is considered as a useful antibiotic to treat infections in the ICU.
Keywords: MRSA; VRE; antibacterial drugs; intensive care unit; linezolid.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Ford CW, Zurenko GE, Barbachyn MR. The discovery of linezolid, the first oxazolidinone antibacterial agent. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2001;1(2):181–199. - PubMed
-
- Barbachyn MR, Toops DS, Grega KC, et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of new tropone-substituted phenyloxazolidinone antibacterial agents 2. Modification of the phenyl ring – the potentiating effect of fluorine substitution on in vivo activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1996;6(9):1009–1014.
-
- Zyvox [package insert] Kalamazoo, MI: Pharmacia-Upjohn; 2004.
-
- Batts DH. Linezolid-a new option for treating Gram-positive infections. Oncology. 2000;14(8 Suppl 6):23–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

