Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of FoxM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 29950861
- PMCID: PMC6016270
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S155541
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of FoxM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: Recently, the abnormal expression of FoxM1 has been found in many malignant tumors. However, the clinicopathological and prognostic value of FoxM1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients remains controversial. We conducted a meta-analysis to establish the relationship between FoxM1 expression and the clinicopathological features and prognostic value in patients with HCC.
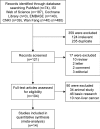
Methods: An electronic search for relevant articles was conducted according to a set of criteria in the PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, EMBASE, Chinese CNKI and Chinese WanFang databases. The correlation data between FoxM1 expression and clinicopathological features and survival outcomes were analyzed. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) and hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs were calculated using STATA14.2.
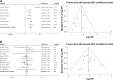
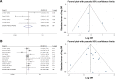
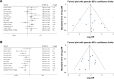
Results: A total of 14 studies comprising of 2,036 patients were enrolled in this meta-analysis. The results showed that FoxM1 expression was related to the incidence, tumor size (>5 cm), vascular invasion, differentiation and TNM stage. Moreover, overexpression of FoxM1 indicated a poor 3- and 5-year overall survival rate (OS) and recurrence-free survival rate (disease-free survival rate).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis indicated that FoxM1 expression was associated with incidence, tumor size (>5 cm), vascular invasion, differentiation and TNM stage. Accordingly, FoxM1 may be a reliable prognostic biomarker for patients with HCC. However, additional high-quality studies are still needed to further support these findings.
Keywords: FoxM1; clinicopathological feature; hepatocellular carcinoma; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



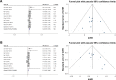


Similar articles
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Nanog in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2018 Feb;477:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.11.037. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Clin Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29198990
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of OCT4 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Dec 21;11:47-57. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S151390. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 29317833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological significance and prognostic role of p-STAT3 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Mar 5;11:1203-1214. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S156198. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29551899 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Beclin1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Apr 27;11:2387-2397. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S151751. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29740214 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of MACC1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):4769-77. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Significance of the Duality of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 17;14(2):444. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020444. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance to Antiangiogenic Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Impact.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;14(24):6245. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246245. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of FOXM1 and Aurora-A predicts prognosis and sorafenib efficacy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2020;28(3):341-350. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190507. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 32390596 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced expression of microRNA-139-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma results in a poor outcome: An exploration the roles of microRNA-139-5p in tumorigenesis, advancement and prognosis at the molecular biological level using an integrated meta-analysis and bioinformatic investigation.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):6704-6724. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11031. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31807180 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive clinicopathological significance and putative transcriptional mechanisms of Forkhead box M1 factor in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Nov 25;21(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03250-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38001498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379(982):1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Avila MA, Berasain C, Sangro B, Prieto J. New therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25(27):3866–3884. - PubMed
-
- Myatt SS, Lam EW. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(11):847–859. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

