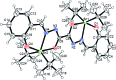
Crystal structure of (μ- trans-1,2-bis-{2-[(2-oxido-phen-yl)methyl-idene]hydrazin-1-yl-idene}ethane-1,2-diolato-κ3O, O', N)bis-[di- tert-butyl-tin(IV)]
- PMID: 29951233
- PMCID: PMC6002830
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018007077
Crystal structure of (μ- trans-1,2-bis-{2-[(2-oxido-phen-yl)methyl-idene]hydrazin-1-yl-idene}ethane-1,2-diolato-κ3O, O', N)bis-[di- tert-butyl-tin(IV)]
Abstract
The binuclear complex, [Sn2(C4H9)4(C16H10N4O4)], contains two Sn4+ ions, connected by doubly N-deprotonated oxalylbis[(2-oxido-benzyl-idene)hydrazide] ligands, and each Sn4+ ion is linked to two tert-butyl groups. The coordination sphere of each Sn atom is best described as a distorted trigonal bipyramid. Each stannic ion in the complex is in a C2O2N environment. The two homologous parts of the doubly deprotonated ligand are located in trans positions with respect to the C-C bond of the oxalamide group. The oxalamide group exhibits an asymmetric coordination geometry, as seen by the slight difference between the C-O and C-N bond lengths. The three-dimensional network is a multilayer of complex mol-ecules with no strong supramolecular inter-actions.
Keywords: Schiff base; crystal structure; tin.
Figures
References
-
- Addison, A. W., Rao, T. N., Reedijk, J., van Rijn, J. & Verschoor, G. C. (1984). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 1349–1356.
-
- Beltrán, I. H., Damian-Zea, C., Hernández-Ortega, S., Nieto-Camacho, A. & Ramírez-Apan, M. T. (2007). J. Inorg. Biochem. 101, 1070–1085. - PubMed
-
- Bruker (2016). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
-
- Hong, M., Yin, H.-D., Chen, S.-W. & Wang, D.-Q. (2010). J. Organomet. Chem. 695, 653–662.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous