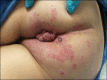
Development of Drug-Induced Inverse Psoriasis in a Patient with Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 29951562
- PMCID: PMC6013682
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.2018.47
Development of Drug-Induced Inverse Psoriasis in a Patient with Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Crohn's disease is difficult to manage and often requires multiple medications. While these drugs vastly improve quality of life, physicians must monitor for adverse events. We report a case of a flare of inverse psoriasis after 15 months of treatment with ustekinumab. This is the third reported case of a flare of drug-induced psoriasis with ustekinumab, and it is the first reported case with an inverse presentation; however, the clinical picture is confounded by concomitant use of hydroxychloroquine. Inverse psoriasis is a rare variant of drug-induced psoriasis of which physicians must be cognizant while treating patients with Crohn's disease.
Figures
References
-
- Crowson AN, Brown TJ, Magro CM. Progress in the understanding of the pathology and pathogenesis of cutaneous drug eruptions: Implications for management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(6):407–28. - PubMed
-
- Tsankov N, Angelova I, Kazandjieva J. Drug-induced psoriasis: Re-cognition and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000;1(3):159–65. - PubMed
-
- Guerra I, Algaba A, Pérez-Calle JL, et al. . Induction of psoriasis with anti-TNF agents in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A report of 21 cases. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6(5):518–23. - PubMed
-
- Omland SH, Gniadecki R. Psoriasis inversa: A separate identity or a variant of psoriasis vulgaris? Clin Dermatol. 2015;33(4):456–61. - PubMed
-
- Chua-Aguilera CJ, Moller B, Yawalkar N. Skin manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and spondyloarthritides. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;53(3):371–93. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources