How Do Intrinsically Disordered Viral Proteins Hijack the Cell?
- PMID: 29952542
- PMCID: PMC6054125
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00622
How Do Intrinsically Disordered Viral Proteins Hijack the Cell?
Figures
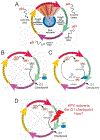
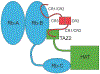
References
-
- Bellacchio E, and Paggi MG (2013) Understanding the targeting of the RB family proteins by viral oncoproteins to defeat their oncogenic machinery, J. Cell. Physiol 228, 285–291. - PubMed
-
- zur Hausen H (2009) Papillomaviruses in the causation of human cancers -- a brief historical account, Virology 384, 260–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

