A new 3D printed titanium metal trabecular bone reconstruction system for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- PMID: 29952948
- PMCID: PMC6039592
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011088
A new 3D printed titanium metal trabecular bone reconstruction system for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Abstract
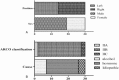
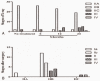
Presently, biomechanical support therapy for the femoral head has become an important approach in the treatment of early osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH). Previous studies have reported that the titanium metal trabecular bone reconstruction systems (TMTBRS) achieved satisfactory clinical results for the treatment of early femoral head necrosis. Electron beam melting technology (EBMT) is an important branch of 3D printing technology, which enables the construction of an interface that is required for support of bone in-growth. However, the effect of TMTBRS created using EBMT for clinical applications for early ONFH is still unknown. At present, there are no reports on this topic worldwide. The purpose of this study was to assess the safety of a new 3D printed TMTBRS implant and to evaluate its clinical efficacy in early ONFH.Thirty patients who underwent surgery for ONFH were selected. The stages of ONFH were classified according to the Association Research Circulation Osseus (ARCO) classification. They were followed-up and radiological examination was performed at 6, 12, and 24 months post-surgery to assess TMTBRS stability and bone growth in the bone trabecular holder portion surface. To evaluate hip function, postoperative Harris and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores were used.The postoperative Harris score increased significantly and VAS score decreased significantly at the 12-month follow-up compared to the 24-month follow-up, wherein the Harris score declined slightly and the VAS score was slightly elevated with the aggravation of ONFH. With the passage of time, postoperative improvement rates were 100% for IIA, 70% for IIB, and 0% for IIC. Hip-preserving rates were 100% for IIA, 100% for IIB, and 50% for IIC.The effect of TMTBRS treatment for early ONFH in ARCO IIA and ARCO IIB is satisfactory. However, it is not recommended for a relatively large area of necrosis such as in ARCO IIC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures








References
-
- Gatin L, Rogier DMA, Mary P, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a proposed new treatment in homozygous sickle cell disease. Hemoglobin 2016;40:01–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhou G, et al. Fibular allograft for osteonecrosis prevention in the management of femoral neck fractures: clinical outcome and biomechanical evaluation. J Biomater Tiss Eng 2015;5:937–41.
-
- Bravo D, Wagner ER, Larson DR, et al. No Increased risk of knee arthroplasty failure in patients with positive skin patch testing for metal hypersensitivity: a matched cohort study. J Arthroplasty 2016;31:1717–21. - PubMed
-
- Shim JH, Yoon MC, Jeong CM, et al. Efficacy of rhBMP-2 loaded PCL/PLGA/beta-TCP guided bone regeneration membrane fabricated by 3D printing technology for reconstruction of calvaria defects in rabbit. Biomed Mater 2014;9:065006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

